Figure 1.
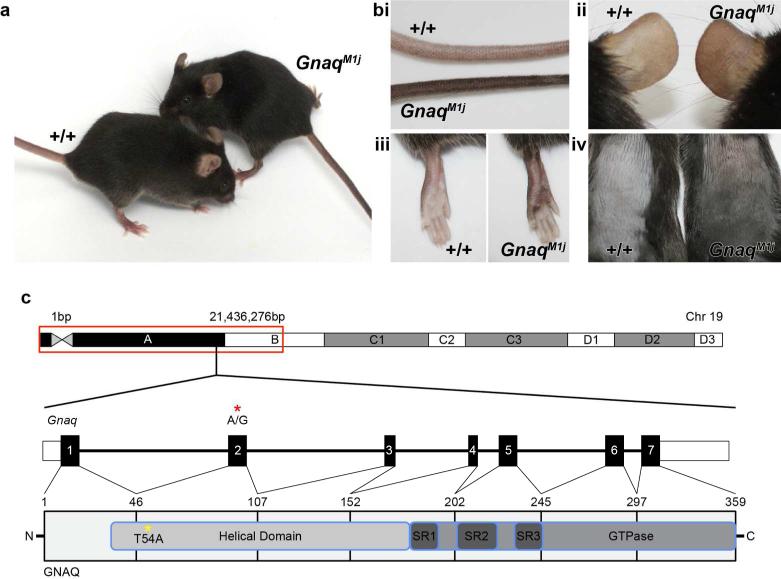
Mutant mice (Left, A) compared with wildtype controls (Right, C57BL/6J +/+) had unusually darkly pigmented tails (i), ears (ii), lower legs (iii), foot pads (iii) and dorsal skin (iv). (C) SNP mapping identified a 21Mb interval on proximal Chr 19 that includes the causative variant. Gnaq, located within the mapping interval, consists of 7 exons. Targeted exome sequencing identified an A to G substitution in exon 2 of this gene (red asterisk; GAGCA\TCCTT), which results in a T54A change in the helical domain of GNAQ (yellow asterisk).