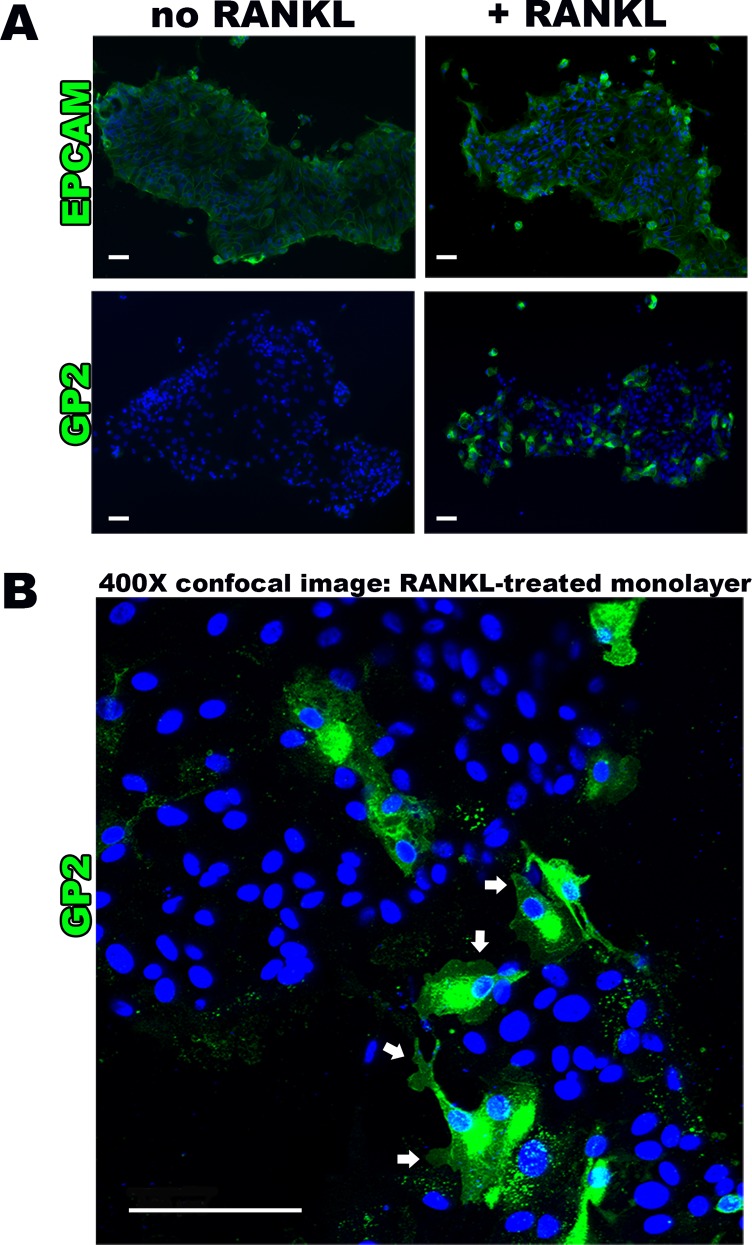
Fig 2. RANKL induces M cell surface marker presence and typical morphology.
(A) Epifluorescense imaging (100X magnification) of human intestinal monolayers showing uniform expression of epithelial cell surface marker EPCAM in no RANKL and RANKL-treated monolayers, confirming epithelial origin. This is in comparison to M cell surface marker GP2 absence in no RANKL group versus positive GP2 staining in RANKL monolayer groups. (B) Confocal microscopy assessment (400X magnification) of immunostained RANKL treated monolayers showing membrane surface and cytoplasmic GP2 staining, demonstrating the characteristic M cell morphology of pseudopod-like projections (white arrows). Scale bar 100 μm.