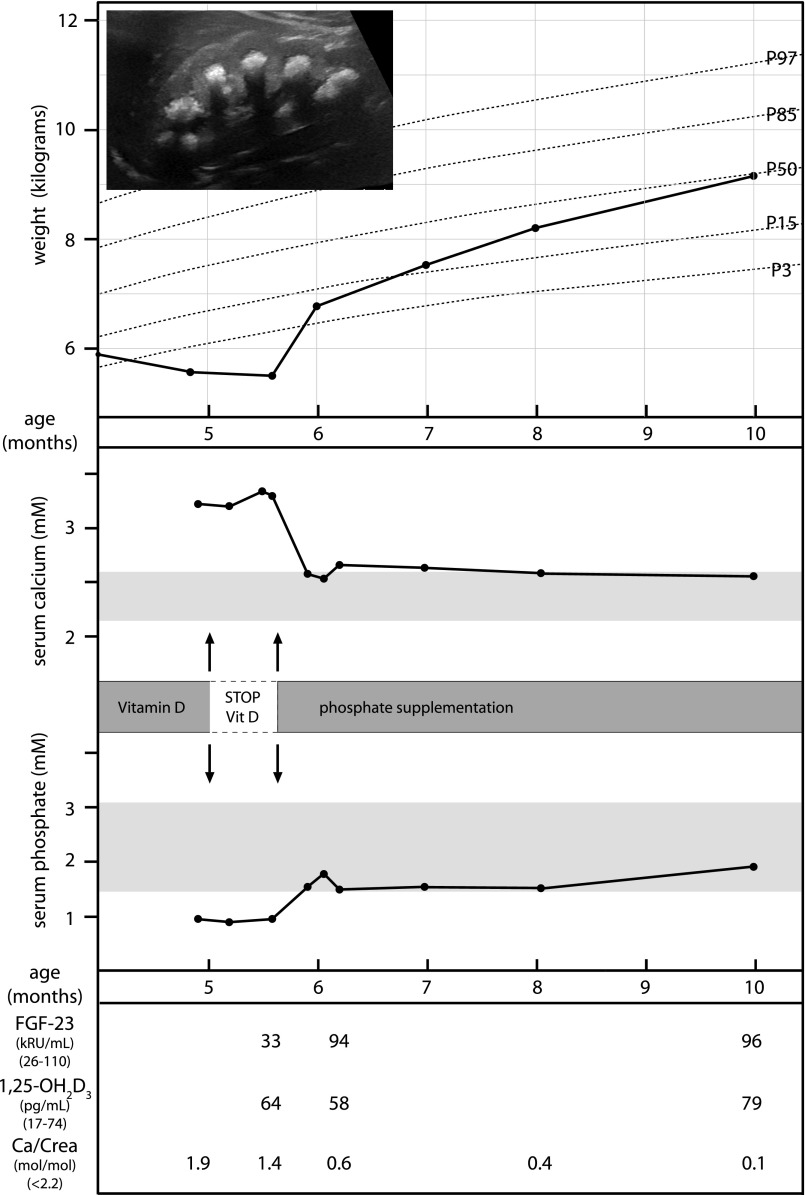
Figure 3.
Clinical course of patient F9.1 during acute disease manifestation. Whereas rehydration and omitting of vitamin D prophylaxis did not lead to correction of hypercalcemia and clinical improvement, phosphate supplementation implemented after genetic diagnosis of SLC34A1 mutations resulted in normophosphatemia, a normalization of calcium metabolism, a reduction in calcium excretion, as well as a rapid clinical recovery and weight gain. The inset shows severe medullary nephrocalcinosis on renal ultrasonography in this infant.