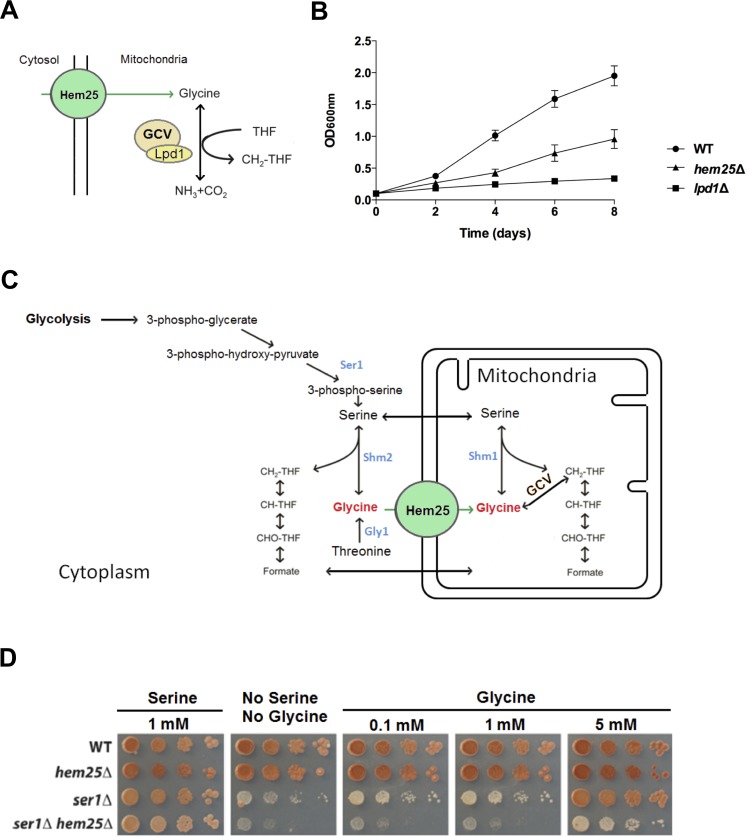
Fig 2. Hem25 is required for the effective import of glycine into mitochondria.
A) Glycine can serve as the sole nitrogen source in S. cerevisiae. The GCV converts glycine to NH3, as the GCV resides in the mitochondria the use of glycine as a nitrogen source requires efficient uptake of glycine into the mitochondria. B) Inactivation of the HEM25 gene in yeast substantially decreased their ability to grow on glycine as the sole nitrogen source. Cells were grown in SD medium containing 30 g/l glycine as nitrogen source. Growth was determined by optical density (OD) of the culture at 600 nm. Data shown are the mean ± SEM for four replicates for wild type and lpd1Δ cells and nine replicates for hem25Δ cells. C) Serine is synthesized from the glycolytic intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate through a series of reactions that includes phosphoserine transaminase (PSAT1 in humans, Ser1 in S. cerevisiae). Serine is normally the main source of one carbon units (CH2-THF, 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate and its metabolites) in cells. Inactivation of the SER1 gene in yeast results in yeast cells that are auxotrophic for serine. Glycine supplementation can also overcome a mutation in the SER1 gene as glycine can serve as a metabolic source for both serine and one carbon units. However, this capacity depends entirely on mitochondrial glycine import. The import of glycine into the mitochondria can generate one carbon units in the form of CH2-THF through the activity of the glycine cleavage system (GCV). In addition, mitochondrial serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT2 in humans, Shm1 in yeast) catalyzes the synthesis of serine from glycine and CH2-THF, with serine exported into the cytoplasm to be consumed for several anabolic pathways including the synthesis of CH2-THF. Simultaneously, CH2-THF generated from glycine is oxidized to formate and also exported into the cytoplasm as a source of cytoplasmic one carbon units. D) An inability to import glycine into the mitochondria prevents glycine supplementation from providing serine and one carbon units to cells with an inactivated SER1 gene. This was found to be the case upon inactivation of the yeast HEM25 gene. Cells were grown to mid-log phase in SD medium containing 1 mM serine, and 1:10 serial dilutions plated on SD medium with no supplements or supplemented with serine or glycine.