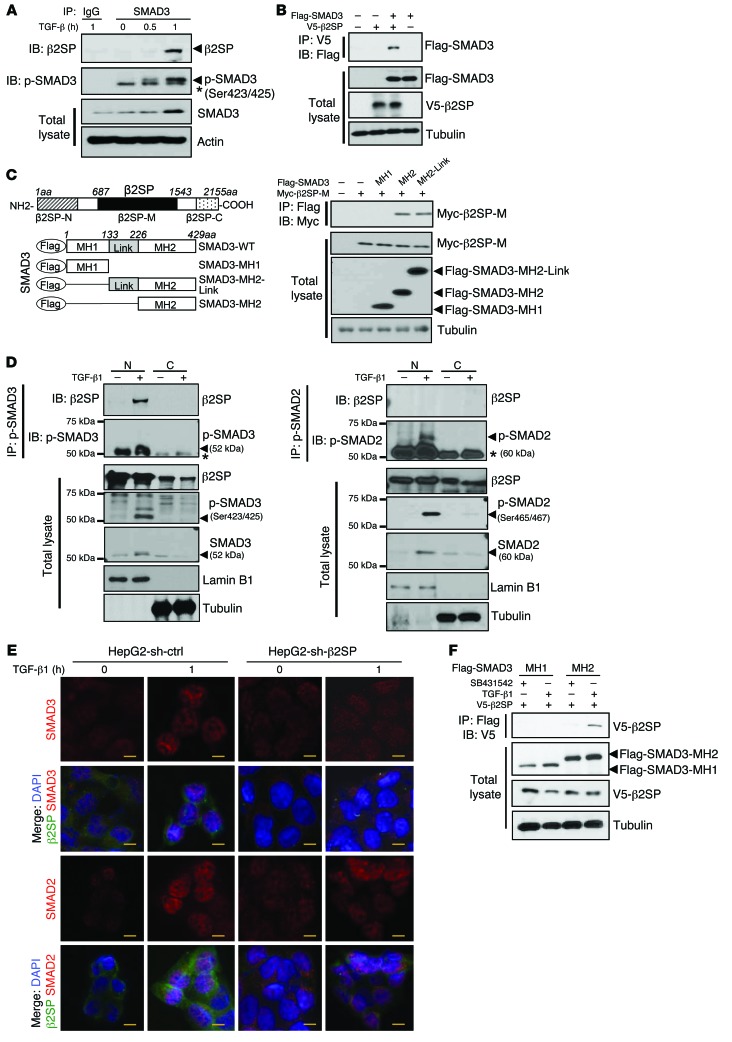
Figure 3. β2SP is required for SMAD3 nuclear translocation in BWS cells.
(A) Interaction of β2SP and SMAD3 is TGF-β dependent. HepG2 cells were treated with 200 pM TGF-β1 for the indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a SMAD3 antibody and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Asterisk designates nonspecific bands. (B) β2SP interacts with SMAD3. SNU398 cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a V5 antibody and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (C) β2SP interacts with SMAD3 MH2 domain. SNU398 cells were cotransfected with indicated plasmids. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a Myc antibody and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. (D) Interaction of β2SP and p-SMAD3 in cell nucleus. Cell lysates were isolated as nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) compartments. HepG2 cells were treated with 200 pM TGF-β for 2 hours. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a p-SMAD3 antibody or a p-SMAD2 antibody and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Asterisk designates IgG heavy chain bands. (E) Knockdown of β2SP compromises TGF-β–induced SMAD3, but not SMAD2, nuclear translocation. HepG2 shRNA control cells and shRNA-β2SP stable cells were treated with 200 PM TGF-β for 1 hour. Immunofluorescent staining was performed to detect β2SP, SMAD3, or SMAD2. Scale bars: 40 μm. (F) TGFBR1 inhibitor SB431542 blocks the interaction of β2SP and SMAD3. SNU398 cells were cotransfected with indicated plasmids and were treated with 5 μM TGFBR1 inhibitor SB431542 overnight. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with a Flag antibody and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies. Data are representative of 3 (A, B, and D), 2 (C), and 1 (F) independent experiments.