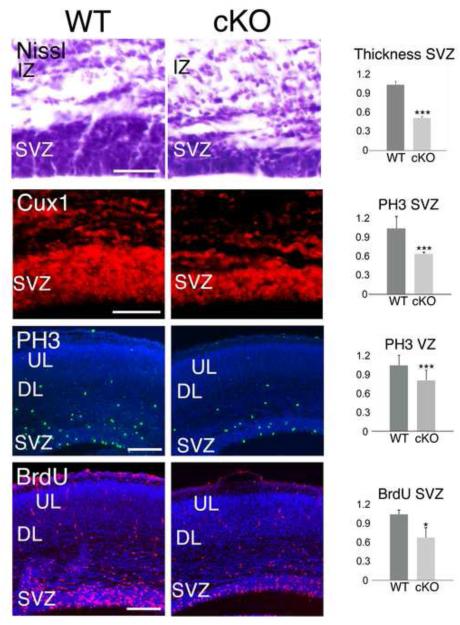
Figure 4. Conditional deletion of MDGA1 from cortical progenitors results in significant reduction of thickness and proliferation in the neurogenic niches.
Shown are coronal sections of E16.5 cortex from wild type (WT) and mice with a conditional deletion of MDGA1 using Nestin-Cre (cKO), demonstrating that both the thickness of the subventricular zone (SVZ, Nissl, Cux1) and proliferation in the SVZ (PH3, BrdU) are significantly reduced in the cKO. Nissl staining and immunofluorescence for the SVZ marker Cux1 shows a significant reduction in the thickness of the SVZ in the cKO versus WT (0.53±0.01, p= 0.005***, N=4). The number of PH3+ cells is also significantly reduced by 45% in the SVZ (0.559±0.03, p=0.0006***, N=4), and by 21% in the VZ (0.789±0.06, p=0.005***, N=4) in the cKO compared to WT. A 2-hour pulse of BrdU shows a reduction in BrdU incorporation by 35% in the SVZ of the cKO compared to WT (0.71±0.076, p=0.04*, N=4). Abbreviations: DL: deeper layers; IZ: intermediate zone; UL: upper layers; VZ: ventricular zone. Scale bars: Nissl and Cux1 panels (50 μm) and PH3 and BrdU panels (100 μm).