Figure 1. Genetic-pharmacological and intersectional genetic strategies used to label Brn3b-positive cranial nerve neurons.
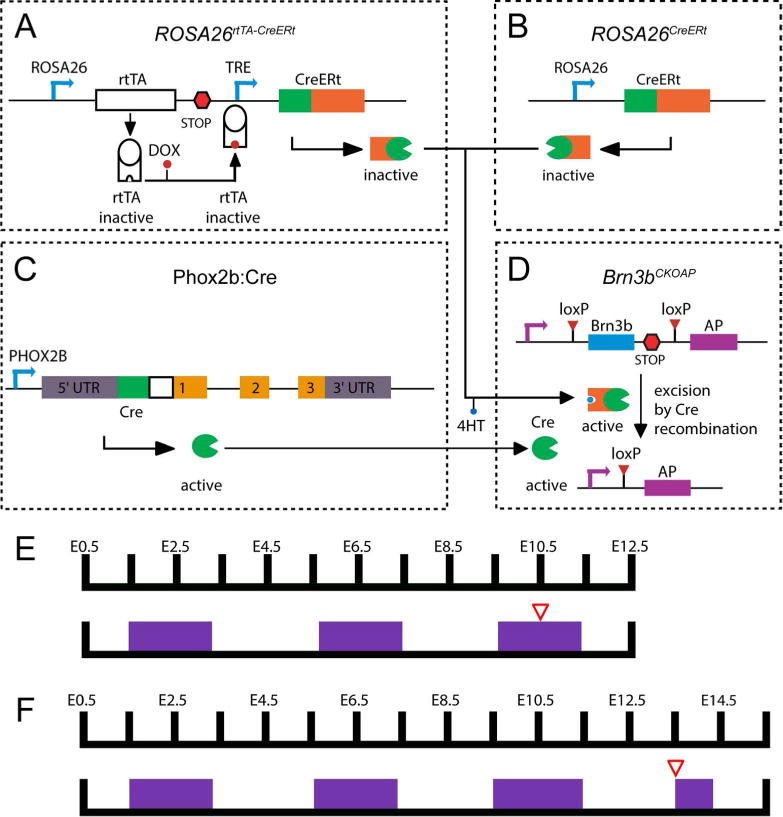
The Cre dependent Brn3b conditional knock-in AP reporter mouse line (A) was crossed to three alternative genetic drivers in order to obtain ubiquitous dense (B), neuronal subpopulation specific (C) or ubiquitous sparse (D) Cre activity. A, Conditional Knock-in reporter construct targeted at the Brn3b locus (Brn3bCKOAP). B, Near complete recombination was induced by 4HT induction of the CreERt activity from the R26CreERt knock-in allele. C, BAC transgenic line expressing constitutively active Cre in Phox2b positive neurons. D, Sparse random recombination was achieved by dual pharmacological control of a R26rtTA-CreERt knock-in construct. E, F Examples of dual pharmacological control regime used for Cre activity control in R26rtTA-CreERt; Brn3bCKOAP crosses (D × A). Plugged females were given regular feed alternating with 0.2 mg/g Dox chow (purple boxes) every two days, beginning with the day the plug was found (E0.5). 12.5 – 50 μg 4HT injected intraperitoneally two days prior to embryo harvesting (red triangle), at either E12.5 (E) or E15.5 (F).
