Figure 3. Brn3b expression in developing retinal ganglion cells.
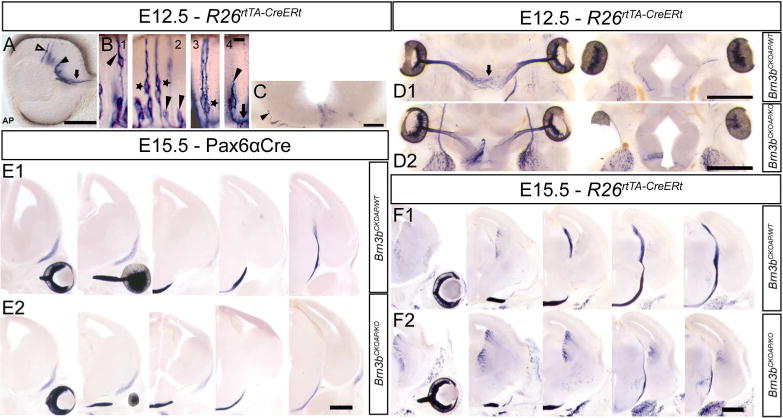
A, Optic cup section with sparsely labeled Brn3bAP RGCs at E12.5. RGCs at different developmental time points: columnar stage (hollow arrow), cells in the RGC layer with retracted ventricular end feet (black arrow head), cells projecting into the optic nerve (black arrow). B, Brn3bAP RGCs in intermediate stages of migration towards the GCL and ventricular (arrow head) process retraction (1). Note the presence of pairs of Brn3bAP RGCs (star) whose ventricular processes are cofasciculated (2) or closely apposed (3). End foot retraction (black arrowhead) and axon extension (black arrow) (4). C, Coronal section at the level of the optic chiasm at E12.5, ipsilateral Brn3bAP RGC axon (black arrow head) climbing on exterior wall of the thalamus. D1, D2, Serial horizontal sections at the level of the developing optic chiasm in R26rtTA-CreERt; Brn3bCKOAP/WT (D1) and R26rtTA-CreERt; Brn3bCKOAP/KO (D2) E12.5 littermates. E1, E2, Serial coronal sections at the level of the developing optic tract in Pax6α:Cre; Brn3bCKOAP/WT; (E1) and Pax6α:Cre; Brn3bCKOAP/KO (E2) E15.5 littermates. F1, F2, Serial coronal sections at the level of the developing optic tract in R26rtTA-CreERt; Brn3bCKOAP/WT (E1) and R26rtTA-CreERt; Brn3bCKOAP/KO; (E2) E15.5 littermates. Scale bars: A,C=100μm, B=10μm, D1,D2,E1–F2=500μm
