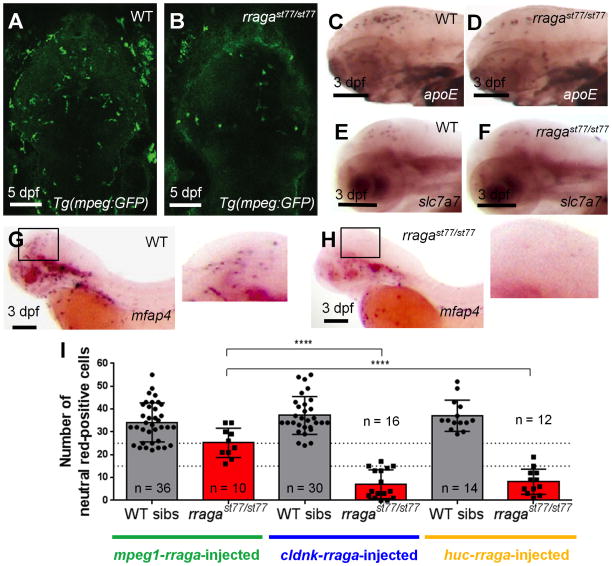
Figure 2. rraga acts autonomously at an early stage of microglia development.
(A–B) Reduction of microglia in rragast77/st77 mutants detected by imaging the mpeg1:EGFP transgene in living wildtype (A) and mutant (B) larvae at 5dpf. Dorsal views, anterior to the top. (C–H) Analysis of other microglia and macrophage markers reveals reduction of microglia at 3 dpf. Probes for apoe (C, D), slc7a7 (E, F), and mfap4 (G, H) were detected by whole mount in situ hybridization. Boxes in G and H show region magnified in the corresponding insets. Lateral views, anterior to the left. (I) Quantification of neutral red stained microglia in rragast77/st77 mutants after transient expression of the wildtype rraga coding sequence under control of regulatory sequences from mpeg1, cldnk, and huc. Only mpeg1-rraga, which drives expression in macrophages and microglia, significantly rescued microglia in the mutants. Dotted line at 15 and 25 shows weak and strong rescue, respectively. ****, P ≤ 0.0001. All scale bars are 50μm. All larvae shown were genotyped by PCR after photography (A–H) or after visually scoring neutral red phenotypes (I).