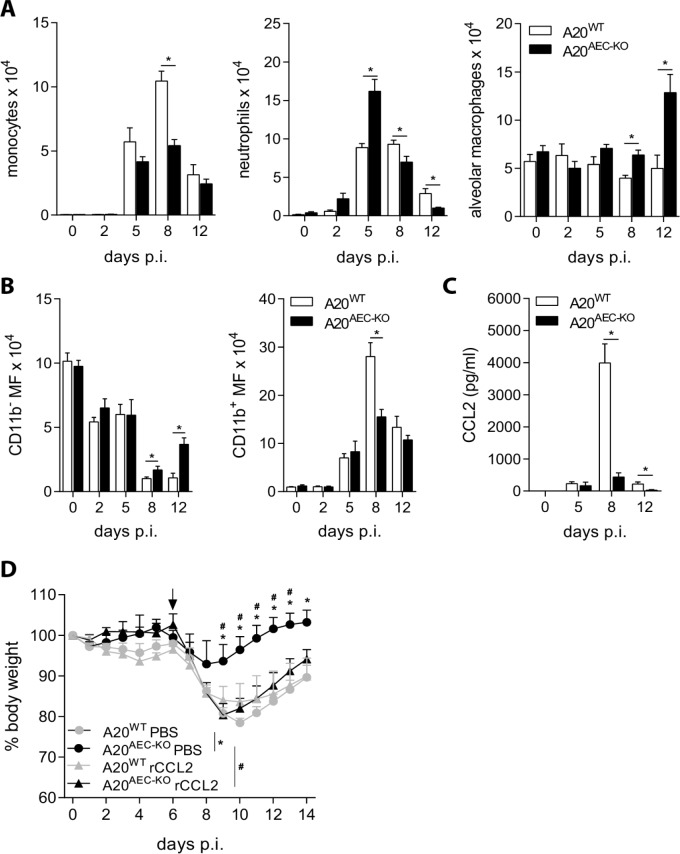
Fig 4. Decreased CCL2 levels protect A20AEC-KO mice against influenza A infection.
(A) Absolute numbers of monocytes, neutrophils and alveolar macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavages (BAL) of A20AEC-KO or A20WT mice at 2, 5, 8 and 12 days post-infection (days p.i.) with 0.05 X LD50 X-47. (B) Absolute numbers of resident CD11b- or recruited CD11b+ macrophages in the lungs of A20WT and A20AEC-KO mice. (C) CCL2 (MCP-1) protein levels in BAL fluid measured by Multiplex immunoassay at indicated time points post-infection. (D) Weight loss of A20AEC-KO and A20WT mice infected with 0.05 X LD50 X-47. At day 6 p.i. (indicated by an arrow) mice received intranasal treatment with 50 μg/kg recombinant CCL2 (rCCL2) or PBS. Data were analysed using Student’s t-test (A, B and C *p < 0.05) and 2-way ANOVA (D, *p < 0.05 for A20AEC-KO PBS vs. A20WT PBS and #p < 0.05 for A20AEC-KO PBS vs A20AEC-Cre rCCL2). Data represent mean ± SEM of at least 3 mice per group. Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments.