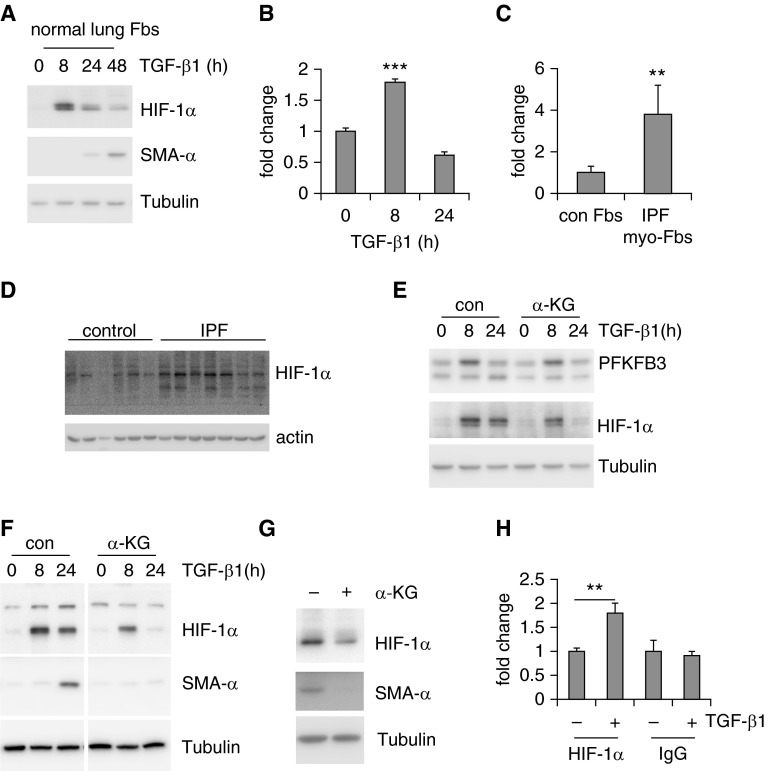
Figure 5.
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-α (HIF-1α) is up-regulated in lung myofibroblasts (myo-Fbs) and required for myo-Fb differentiation. (A) Normal lung Fbs were treated with transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 for 0, 8, 24, or 48 hours and protein levels of HIF-1α, smooth muscle actin (SMA)-α, and tubulin determined. (B) mRNA levels of HIF-1α were determined in TGF-β1–treated MRC-5 cells. n = 3, mean ± SD, ***P < 0.001 by one-way analysis of variance. (C) mRNA levels of HIF-1α were determined in control (con) normal lung Fbs and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) lung myo-Fbs. n = 5–6, mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. (D) Protein levels of HIF-1α and actin were determined in control normal lungs and IPF lungs. (E) Normal lung Fbs were pretreated with α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) (0.5 mM) for 1 hour, followed by TGF-β1 treatment for 0, 8, or 24 hours. Protein levels of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3), HIF-1α, and tubulin were determined. (F) Normal lung Fbs were pretreated with α-KG (0.5 mM) for 1 hour, followed by TGF-β1 treatment for 0, 8, or 24 hours. Protein levels of HIF-1α, SMA-α, and tubulin were determined. The images separated by vertical white lines were derived from the same blots, with unrelated lanes removed. (G) IPF lung myo-Fbs were treated with α-KG (0.5 mM) for 0 or 24 hours. Protein levels of HIF-1α, SMA-α, and tubulin were determined. (H) Normal lung Fbs were treated with TGF-β1 for 0 or 8 hours. The cells were then fixed and lysed. Immunoprecipitations with anti–HIF-1α or -rabbit IgG were performed and DNA in the immunocomplexes purified. The binding of HIF-1α to the HIF-1α responsive element within the SMA-α promoter was quantified by real-time polymerase chain reaction and presented as fold change relative to the untreated control group. n = 3, mean ± SD, **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. Experiments in A–C and E–H were performed two to three times.