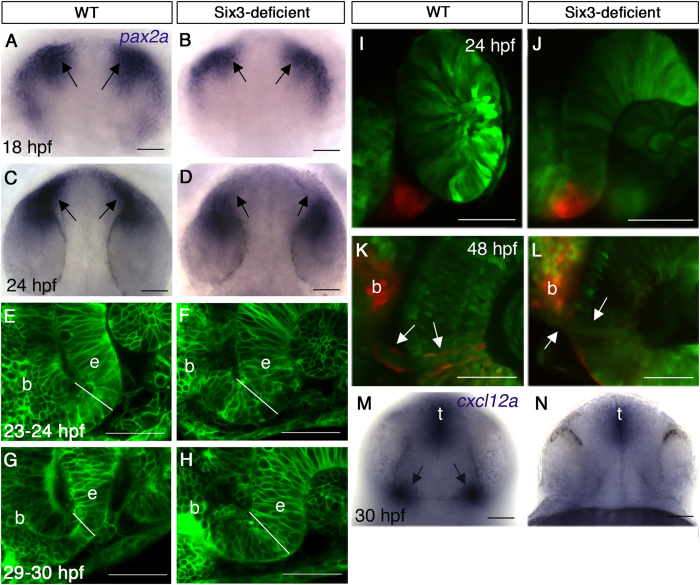
Figure 4. Abnormal optic stalk development in Six3-deficient embryos.
(A–D) WISH for pax2a at 18 hpf (A,B) and 24 hpf (C,D) in WT (A,C) and Six3-deficient embryos (B,D). Arrows in (A–D) point at the OSs. (E–H) Confocal images of OS in live WT (E,G) and Six3-deficient (F,H) embryos at 23–24 hpf (E,F) and 29–30 hpf (G,H). Outlines of all cells are highlighted by expression of membrane-tethered GFP. White lines demarcate OS width at the interface with the retina. (I–L) Confocal images of rx3:Kaede live embryos in WT (I,K) and Six3-deficient (J,L) backgrounds. The OS was photoconverted in these embryos (red). (I,J) Images were captured immediately after photoconversion at 24 hpf. (K,L) Images of the same embryos as in I and J, respectively, at 48 hpf. Arrows point at the periphery of the optic nerve, where only in the WT embryo (K) photoconverted glial cells are present. (M,N) WISH for cxcl12a in WT (M) and Six3-deficient (N) embryos at 30 hpf. Arrows in M point at OS expression of cxcl12a. b, brain; e, eye; t, telencephalon. (A–D) dorsal views anterior up; (E–J) frontolateral views, dorsal up; (K,L) ventral views anterior up; (M,N) frontal views, dorsal up. Scale bars are 50 μm.