Figure 2. Developmental defects in hearts of Crim1Δflox/Δflox embryos.
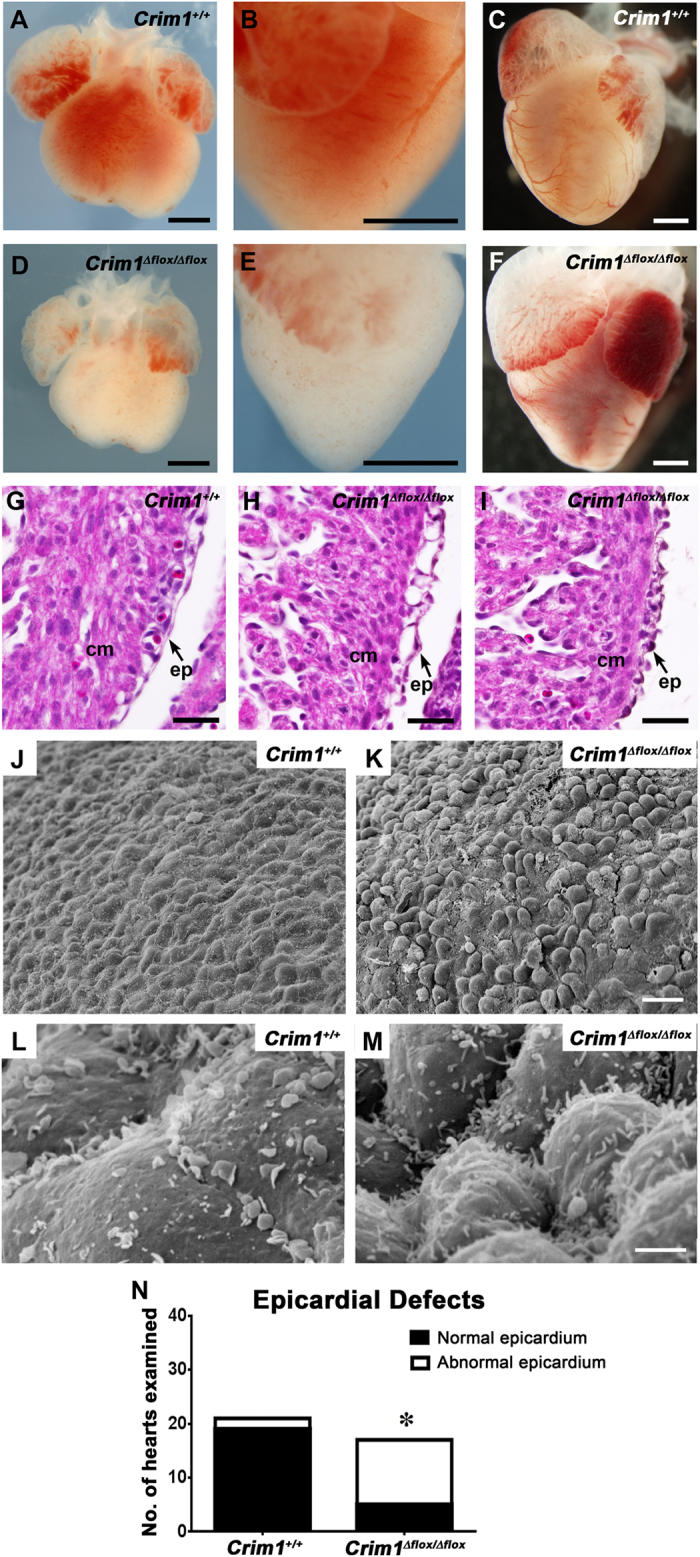
(A,B,D,E) Representative whole-mount views of 14.5 dpc embryonic hearts (A,B, Crim1+/+; D,E Crim1Δflox/Δflox). (B,E) Magnified, left lateral views of (A,D) respectively. (C,F) Representative whole-mount views of 17 dpc embryonic hearts (C, Crim1+/+; (F) Crim1Δflox/Δflox). Note the reduced size of the ventricles in the Crim1Δflox/Δflox heart (D–F). Epicardial defects in Crim1Δflox/Δflox hearts. (G–I) Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections of the ventricular region of 13.5 dpc (G) Crim1+/+ and (H,I) two different Crim1Δflox/Δflox hearts. Note the irregular appearance of the epicardium in Crim1Δflox/Δflox embryos, with one example showing blebbing (H). (J–M) Scanning electron micrographs of the ventricular surface of 13.5 dpc Crim1+/+ (J,L) and Crim1Δflox/Δflox (K,M) hearts. (K) Note the loss of the even spacing of cells of the mesothelial epicardium, and (M) diffusely arranged microvilli. (N) Quantification of penetrance of epicardial defects, specifically either epicardial blebbing or a loss of squamous morphology, between Crim1+/+ and Crim1Δflox/Δflox hearts at 13.5 dpc. Z-score -3.8801. *P < 0.0001. cm, compact myocardium; ep, epicardium. Scale bars; A–F, 500 μm; G-I, 50 μm; J-K, 20 μm; L-M, 2 μm.
