Figure 8. The schematic diagram of the regulatory circuit signaling events involving miR-10a in RA FLSs.
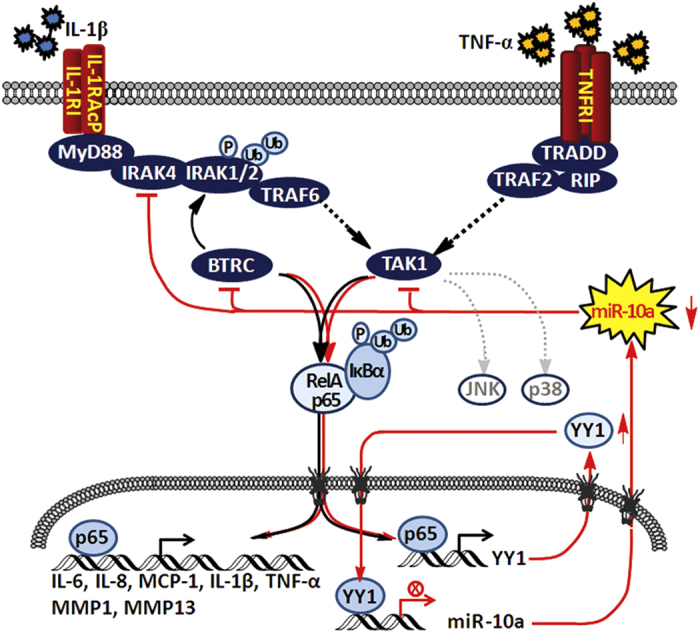
NF-κB is liberated and enters the nucleus of RA FLSs when stimulated with TNF-α or IL-1β. Then, NF-κB is activated and binds to the promoter of YY1 and enhances its expression. The latter protein can act as a transcription factor and repress miR-10a expression by binding to the two YY1-binding sites located in the promoter region of miR-10a. Downregulated miR-10a subsequently promotes NF-κB activation and translocation by targeting IRAK4, TAK1 and BTRC. The activated NF-κB then further downregulates miR-10a via YY1. At the same time, this regulatory circuit promotes the release of various inflammatory factors, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and MCP-1, and the metalloproteinases MMP-1 and MMP13, which are controlled by NF-κB and accelerate the proliferation, migration and invasion of FLSs in RA. The black lines indicate the canonical NF-κB pathway; the red lines indicate the regulatory circuit reported here.
