Table 1. Fractional Occupancy by Growing Polyketide Chains of ACP + KS Active Sites within Individual Modules of Selected DEBS Variantsa.
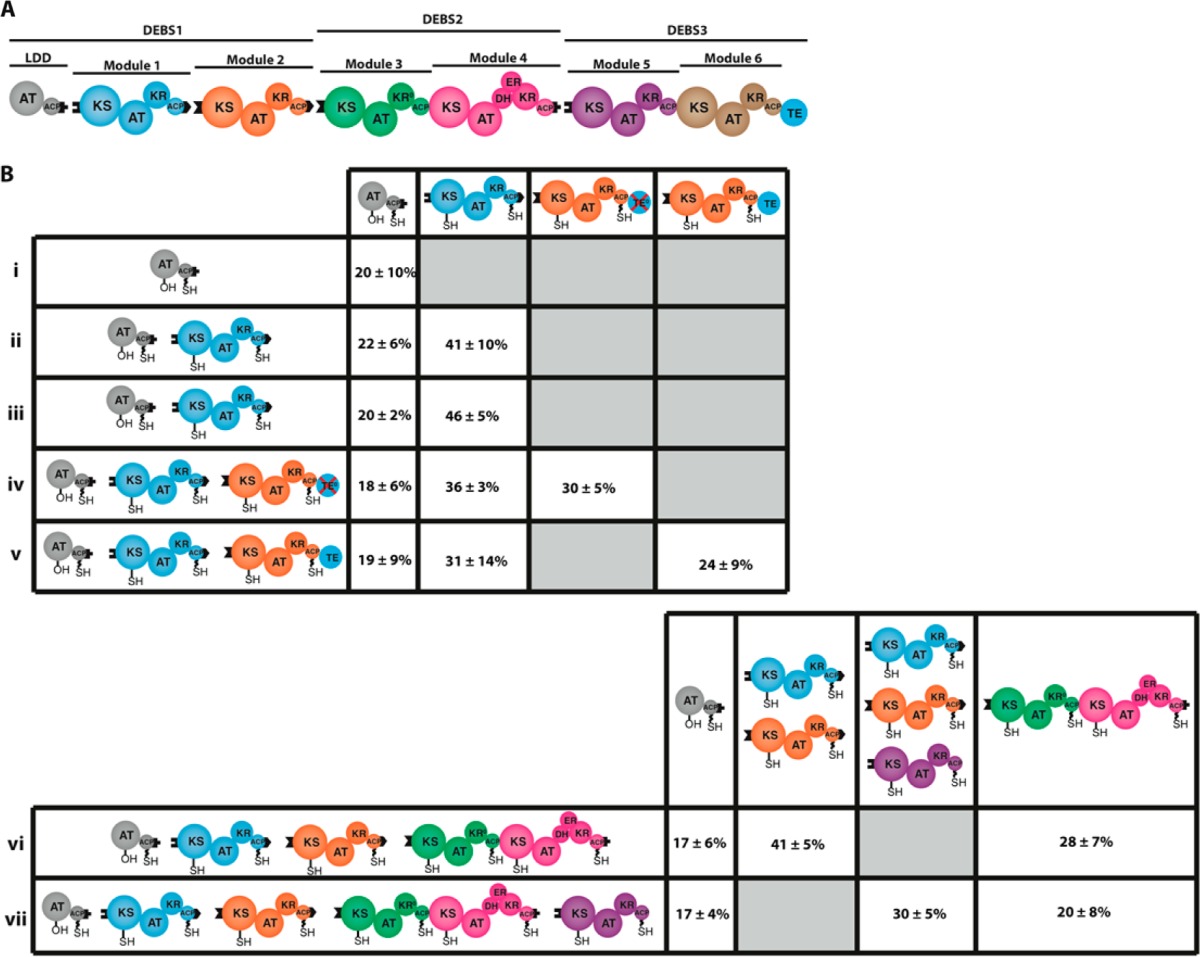
(A) Schematic of the reconstituted DEBS. Each module, as well as the loading didomain (LDD), which primes the most upstream KS domain, and the TE, which catalyzes hydrolytic release of the mature polyketide chain, is shown in a distinct color. DEBS variants were reconstituted as previously described20 from five proteins: LDD, module 1, module 2, DEBS2, and DEBS3. (B) Percent of the combined ACP + KS occupancy within uni- and bimodular derivatives of DEBS (i–v) and percent of the combined ACP + KS occupancy in 4- and 5-module variants (vi, vii). All but one PKS assembly line (v) used in these experiments lacked an active thioesterase (TE) domain. For methodological details, see Supporting Information. In all experiments, DEBS proteins were incubated with 14C-propionyl-CoA and methylmalonyl-CoA, with the exception of i and ii, from which methylmalonyl-CoA was omitted. Occupancy was estimated by radio-SDS–PAGE analysis of each DEBS protein, with measurements in two systems (vi and vii, columns 2 and 3) being performed on multiple comigrating proteins. In these cases, the reported occupancy values were normalized to the corresponding number of thiol carriers. Occupancy values are reported as the mean ± SD (n = 3) of the ACP + KS occupancy after 15 min incubation. For details, see Figures S3–S6, S8, and S10.
