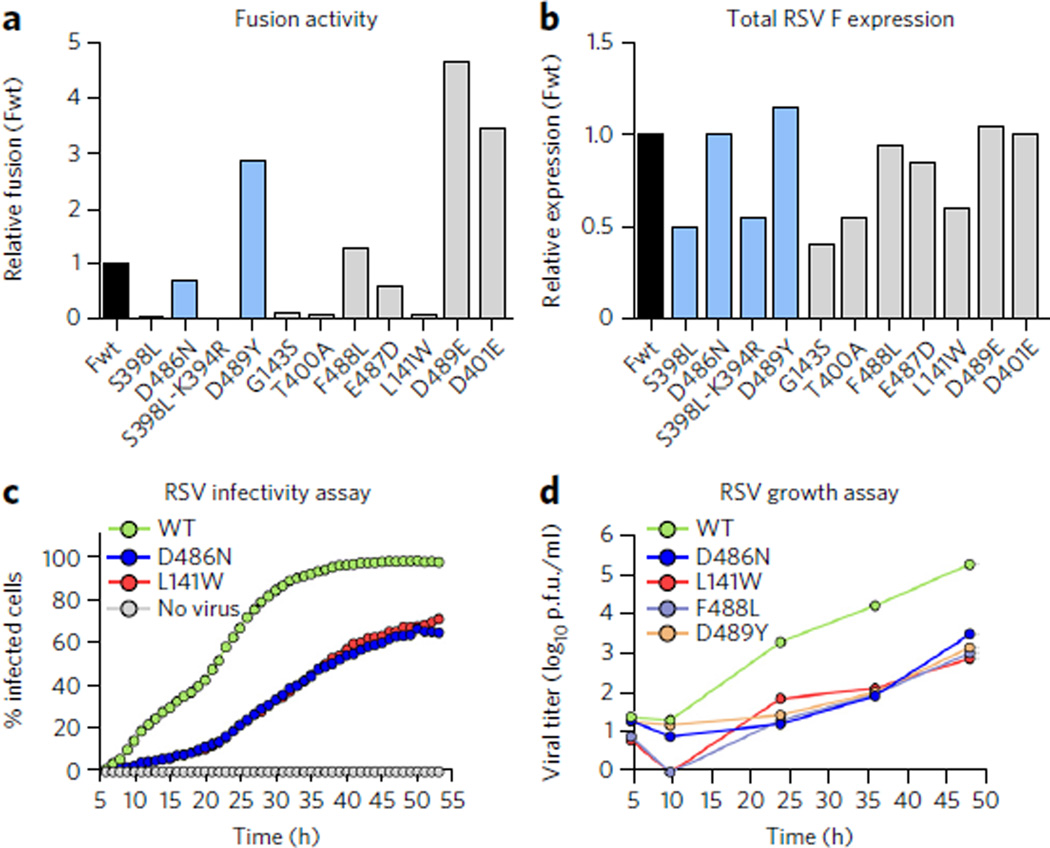
Figure 5. Effects of inhibitor-escape mutations on cell-cell fusion activity and viral fitness.
(a) Relative fusion activity, normalized to wild-type F (Fwt), for RSV F variants containing inhibitor-escape mutations. Data represent the mean of two independent experiments, each replicated six times. (b) Relative RSV F surface expression, normalized to Fwt, as assessed by the binding of the conformation-independent antibody motavizumab to cells transfected in parallel with those used for the fusion assay. Data represent the mean of two independent experiments, each replicated three times. (c) The percentage of A549 cells infected with either wild-type (WT) rgRSV224 or inhibitor-escape variants (D486N or L141W) was measured by analyzing cellular GFP expression in individual cells every 60 min for 48 h starting 5 h after infection. Data represent the mean (n = 2). (d) The growth of WTRSV and inhibitor-escape variants was determined by a plaque titration assay in Vero cells. Data represent the mean of three replicates (n = 1 for each replicate).