Figure 1.
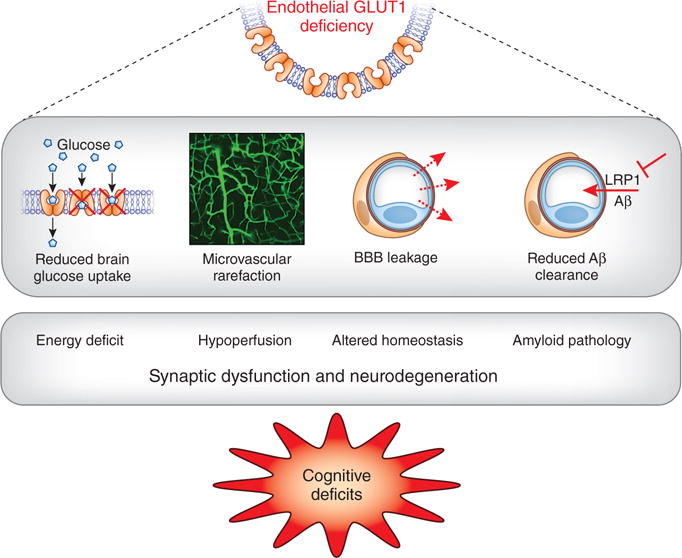
Mechanisms of brain dysfunction and damage caused by GLUT1 deficiency. Endothelial GLUT1 deficiency leads to reduced brain glucose transport, vascular rarefaction and disruption of the BBB, as well as reduced Aβ clearance by suppressing vascular LRP1 expression. These events result in energy deficit, reduced cerebral blood flow (hypoperfusion), altered homeostasis of the brain microenvironment and enhanced amyloid pathology. The resulting synaptic dysfunction and neurodegeneration in turn lead to cognitive deficits.
