Fig. 2.
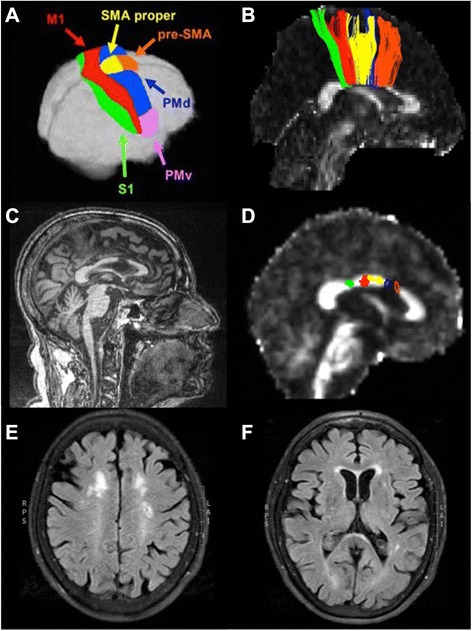
Diffusion tensor imaging: interhemispheric fiber tracts connecting principal, homologous sensorimotor cortical regions. Legend: a The Human Motor Area Template as defined by Mayka et al., 2006. b Interhemispheric fiber tracts from a healthy young adult, color-coded to match the cortical regions shown in panel A, taken from Fling et al., 2013. c Patient’s T1-weighted structural MRI showing an infarct within the anterior body of the corpus callosum. d Patient’s fractional anisotropy map, derived from diffusion weighted data. Fiber tracts were readily identified connecting the S1, M1, and SMA. No fiber tracts connecting either the PMd or the pre-SMA were identified; the blue and orange outlines demonstrate the location in the callosum where these fiber tracts would be expected to cross. e & f White matter hyperintensities within bilateral anterior periventricular regions. S1 = primary somatosensory cortex; M1 = primary motor cortex; SMA = supplementary motor area; PMd = dorsal premotor cortex; PMv = ventral premotor cortex
