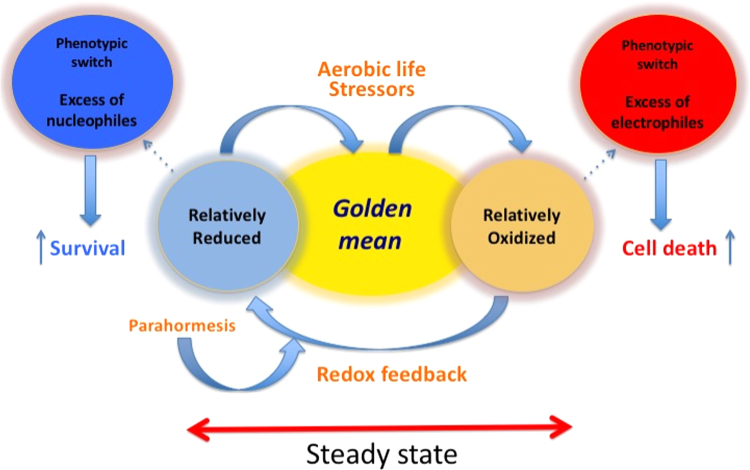
Fig. 1.
The “Golden Mean” of redox homeostasis. A steady-state redox status of the ensemble of redox couples is maintained by metabolic fluxes and redox feedback where electrophiles produced by aerobic life stressors activate the mechanism reestablishing nucleophilic tone. Parahormesis refers to nonessential compounds that support the redox feedback loop activating the nucleophilic response. As long as homeostasis is maintained, there is not a phenotypic switch. In contrast, a phenotypic switch occurs in adaptation when a stable offset of homeostasis takes place. In the scheme two opposing examples of stable offset of redox homeostasis are illustrated; one refers to a more oxidizing environment (e.g. oxidative stress) facilitating cell death, while the other refers to a dramatically more reducing environment (e.g., constitutive activation of Nrf2), facilitating survival. Both conditions are part of pathological phenotypes.