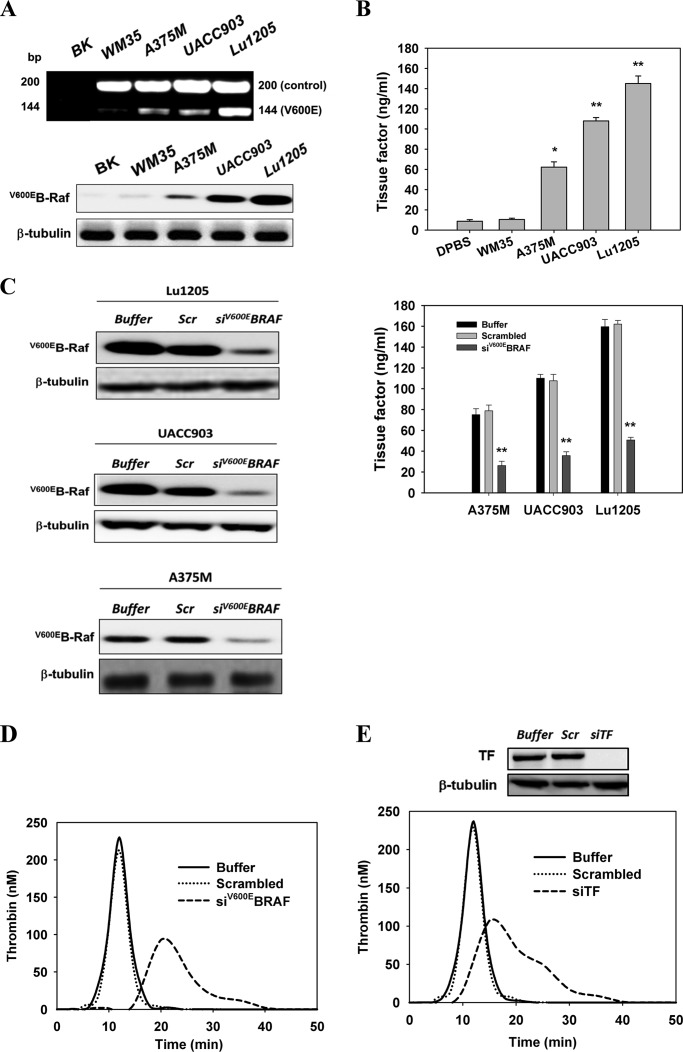
FIGURE 1.
B-Raf(V600E) mutation conferred on melanoma a thrombogenic potential by inducing TF expression. A, ARMS-PCR and Western blotting were used to detect the presence of B-Raf(V600E) in the WM35, A375M, UACC903, and Lu1205 melanoma cell lines. The Fo-Ro primer pair generated a common fragment of 200 bp flanking the mutation site. The Fo-Rimut primer pair generated the 144-bp fragment specific for the B-Raf(V600E) gene. BK, blank no DNA (control). Anti-B-Raf(V600E) (VE1) antibody was used to detect B-Raf(V600E) protein levels. B, cell membrane fractions from four melanoma cell lines were isolated with octyl β-d-glucopyranoside, and TF expression was measured by ELISA. TF levels (nanograms/ml) are shown as means of three independent experiments ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 compared with control cases. C, knockdown of B-Raf(V600E) with siRNA in A375M, UACC903 and Lu1205 cells significantly reduced TF expression. A375M, UACC903, and Lu1205 cells transfected with buffer, scrambled siRNA, or B-Raf(V600E) siRNA were subjected to TF measurement. TF levels (nanograms/ml) are shown as means of three independent experiments ± S.E. **, p < 0.01 compared with control cases. Knockdown efficiency was assessed by Western blotting. Scr, scrambled; siV600EBRAF, B-Raf(V600E) siRNA. D, knockdown of B-Raf(V600E) with siRNA in Lu1205-impaired thrombin generation. Thrombin activities were measured with a calibrated automated thrombogram. E, knockdown of TF with siRNA in Lu1205 cells suppressed thrombin generation. Thrombin activities were measured with a calibrated automated thrombogram. Knockdown efficiency was assessed by Western blotting. siTF, TF siRNA.