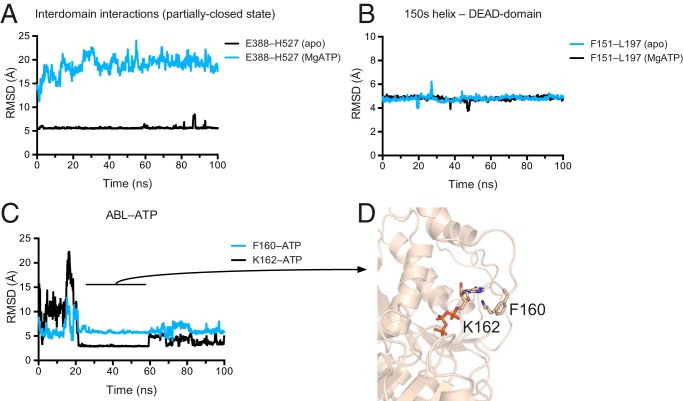
FIGURE 5.
Molecular dynamics simulations suggest a stable interdomain interface and transient ABL-ATP interactions. A, the partially closed structure is stable over a 100-ns trajectory. Separation between the side chains Glu-388 (Cδ) and His-527 (Cγ) is shown for apo DDX3 132–607 (black) and a closed-state model based off the Vasa structure (cyan; PDB 2DB3; see “Experimental Procedures”). RMSD, root mean square deviation. B, the 150′s α-helix forms stable interactions with the DEAD domain (colors as in A). Distance is measured between Phe-151 (Cγ) and Leu-197 (Cγ). C, the ABL makes transient, stable interactions with the adenine group of ATP. Black: distance between the Cγ of Phe-160 and the H2 of ATP; cyan: distance between the Nζ of Lys-162 and the N3 of ATP. In A–C, distances are smoothed over a sliding window of 20 frames. D, structural model of the ABL interacting with ATP at 50 ns of simulation.