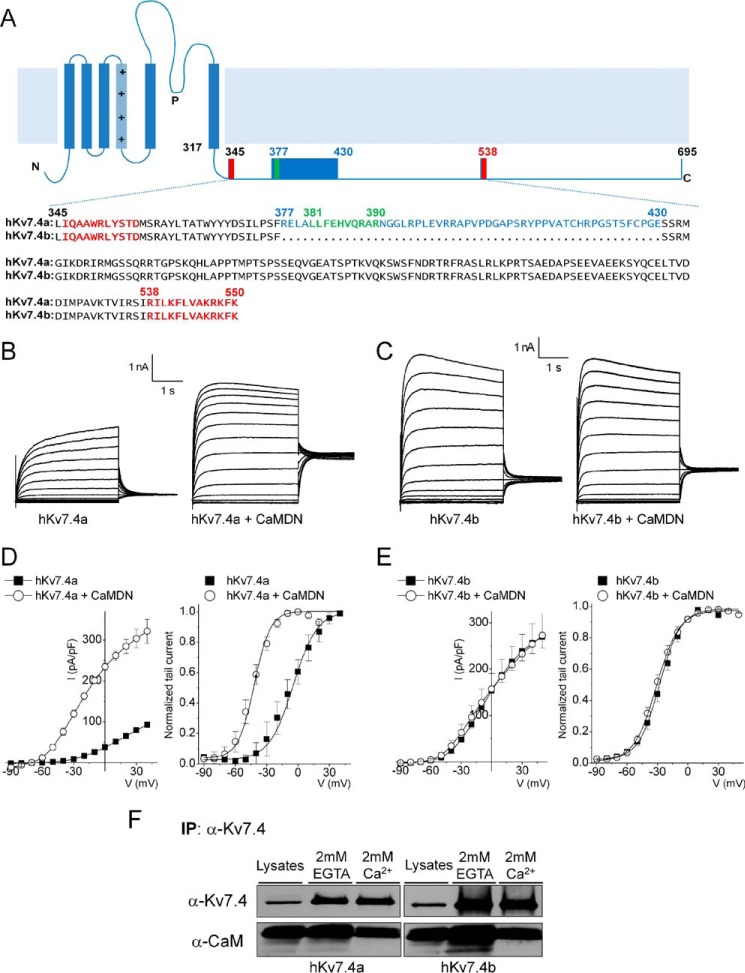
FIGURE 1.
The CaMBD linker is required for the Ca2+/CaM-dependent inhibition of the Kv7.4 current. A, schematic of the Kv7.4 α-subunit structure. The C-terminal sequence alignment of the two isoforms (hKv7.4a, NP_004691; hKv7.4b, NP_751895) is shown. Two known CaM binding domains (CaMBDA and CaMBDB) are marked in red, and a putative CaMBD is marked in green. Spliced alteration of hKv7.4 (hKv7.4a versus hKv7.4b) is indicated in blue. B and C, representative traces showing whole-cell recordings from CHO cells transfected with hKv7.4a and hKv7.4b and co-transfected with either empty vector or CaMDN. The current traces were recorded from a holding potential of −70 mV to step potentials ranging from −90 to 40 mV using voltage increments of 10 mV. Tail currents were recorded at −30 mV. D and E, plots of current density (picoampere/picofarad)-voltage relations of currents (left) were derived from CHO cells expressing hKv7.4a (or hKv7.4b) (closed squares, n = 21) and hKv7.4a (or hKv7.4b) + CaMDN (open circles, n = 21). Normalized tail currents of hKv7.4a and hKv7.4a + CaMDN are plotted against the applied voltage to generate the activation curves (right), which were fitted with a Boltzmann function. The half-activation voltages (V½, in millivolt) and slope factor, k, for hKv7.4a were as follows: −5.7 ± 1.1 and 14.1 ± 0.9 (n = 17); for hKv7.4a + CaMDN they were −42.0 ± 1.8 and 11.4 + 1.5 (n = 19), respectively. The V½ and k values for hKv7.4b were as follows: −28.0 ± 2.6 and 10.5 ± 1.4; and for hKv7.4b + CaMDN they were −31.0 ± 1.4 and 11.1 ± 1.0 (n = 21). F, CHO cells were expressed with either hKv7.4a or hKv7.4b for 24 h. After preparation of cell lysates, immunoprecipitation (IP) was accomplished using hKv7.4 antibody with a buffer containing either 2 mm of CaCl2 or EGTA. Association of hKv7.4 with CaM is Ca2+-independent.