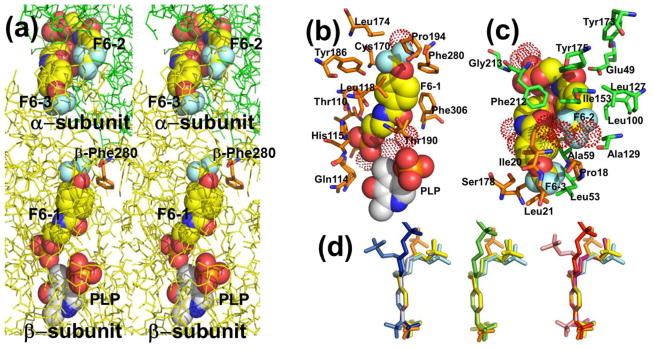
Figure 1.
(a) Stereo view showing F6 bound to the three sites identified in PDB ID: 4WX2 designated as F6-1, F6-2, and F6-3. The location of βPhe280 is also shown. Color scheme: α-subunit green, β-subunit gold, C yellow, and other atoms shown in CPK colors. (b) Details of the atom contacts in the β-subunit between F6-1, site residues, waters and PLP. (c) Details of the atom contacts in the α-subunit between F6-2 and F6-3 and with site residues and waters. Color schemes in (b) and (c); waters shown as red dot surfaces, α-subunit residues, orange; β-subunit residues, green; F6-1, F6-2 and F6-3, C yellow; all other atoms shown in CPK colors; PLP is shown in standard CPK colors. (d) Overlay aligning aromatic rings of F6 molecules from crystal structures PDB IDs: 2CLE, 2CLF, 4WX2, 4ZQC, and 4Y6G. For better visualization, F6 molecules were colored differently; PDB ID: 2CLE (F6-2, cyan), PDB ID: 2CLF (F6-1, orange; F6-2, yellow), PDB ID: 4WX2 (F6-1, blue; F6-2, marine; F6-3, light blue), PDB ID: 4Y6G (F6-1, green; F6-2, limon),PDB ID: 4ZQC (F6-1, red; F6-2, warm pink; F6-3, salmon).