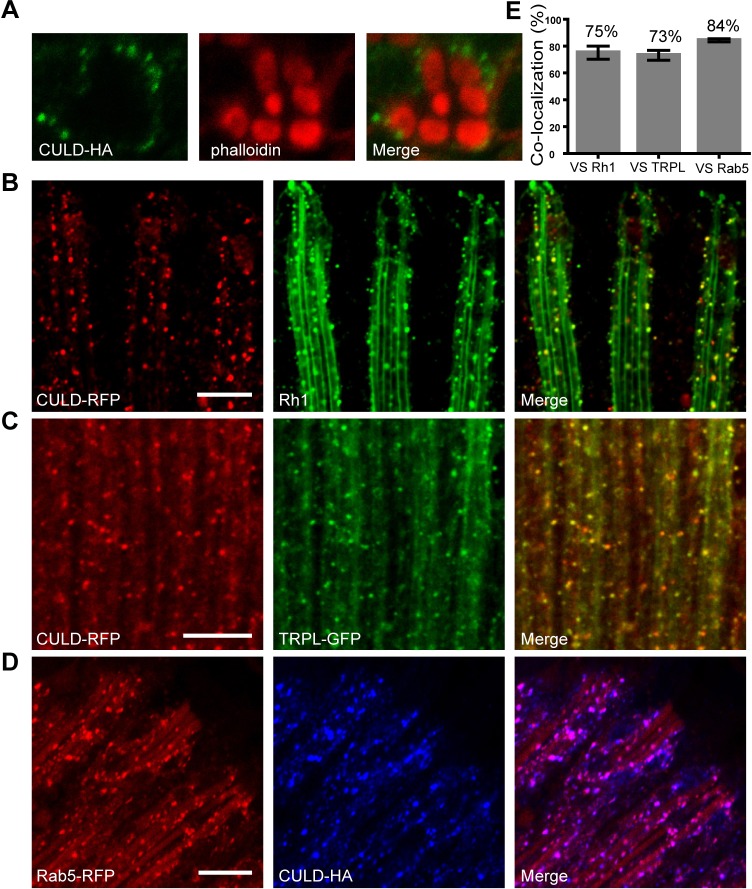
Fig. 5.
CULD locates in TRPL- or Rh1-positive endocytic vesicles in photoreceptor cells. (A) Cross-sectional images of retina dissected from ninaE-culd-HA (cn bw; ninaE-culd-HA) flies were stained with anti-HA antibody for detecting CULD (green) and with phalloidin for labeling the rhabdomere (red). (B) Longitudinal images of retina dissected from cn bw; ninaE- culd-rfp/+ flies were labeled with anti-Rh1 antibody for detecting Rh1 (green) and with anti-RFP for detecting CULD (red). (C) Retinas of cn bw; ninaE-culd-rfp/ninaE-trpl-gfp flies were stained with anti-RFP (red for CULD) and anti-GFP (green for TRPL) antibodies. (D) Retinas of cn bw; ninaE-culd-HA/ninaE-rab5-rfp flies were labeled with anti- HA (blue for CULD) and anti-RFP (red for RFP) antibodies. Two-day-old flies with white eyes were placed in the dark for 12 h before exposed to 2000 Lux white light for 2.5 h. Scale bars: 10 µm. (E) Quantification of the colocalization between CULD and the endocytic Rh1, TRPL and Rab5. Number of vesicles positive for CULD and/or Rh1, TRPL or Rab5 were counted in confocal sections as described in Materials and Methods, and divided by the total number of CULD-positive vesicles. Images of retinas from three different flies and at least five 20 µm×20 µm areas of each retina were quantified. Error bars represent s.d.