Fig. 1.
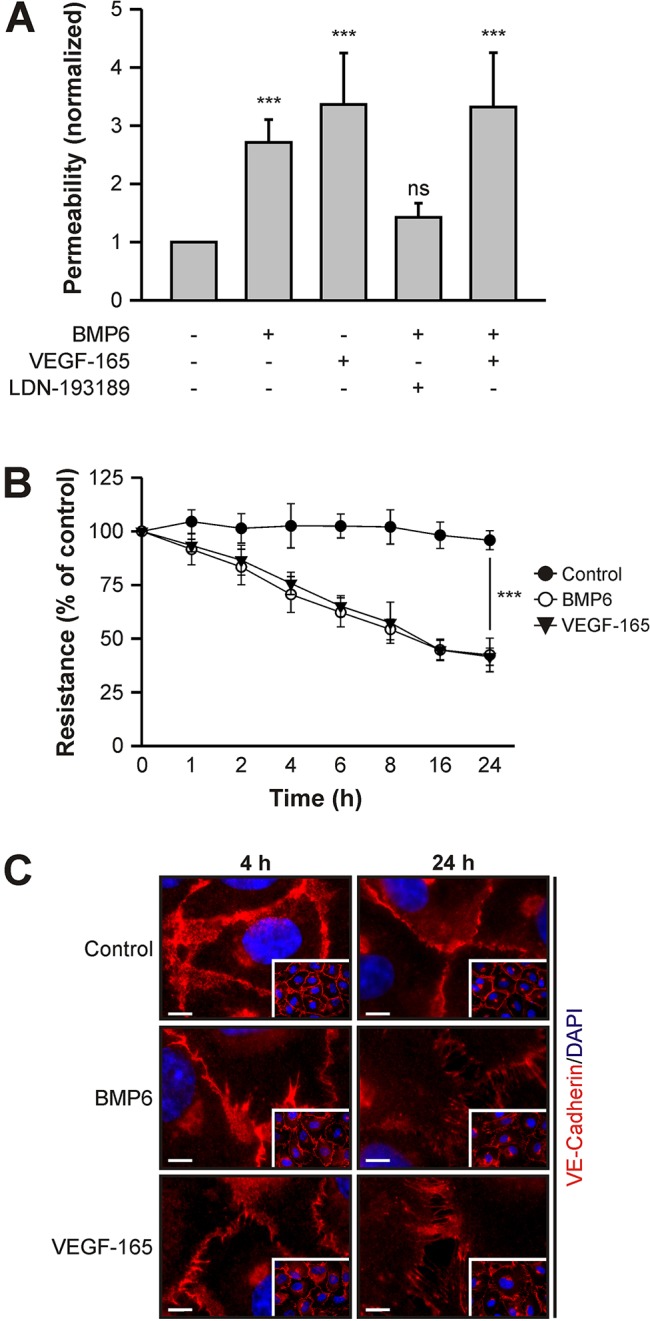
BMP6 induces vascular permeability in vitro. (A) BMP6 increases endothelial cell monolayer solute permeability. HUVECs seeded in transwell inserts were subjected to 10 nM BMP6 or 2 nM VEGF-165 and, as indicated, pharmacological inhibitor (0.5 µM LDN-193189) treatment for 24 h and in vitro transendothelial solute permeability was measured by FITC-Dextran flux. Mean±s.e.m. normalized to untreated control cells from ten biological replicates in three independent experiments. (B) BMP6 stimulation decreases transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER). HUVECs were seeded in transwell inserts and stimulated with growth factors for 24 h. At the indicated time points, TEER was measured. Mean±s.d. normalized to untreated control cells from nine biological replicates in three independent experiments. (A,B) ***P≤0.001; ns, not significant. (C) Immunocytochemical staining of VE-cadherin in HUVECs treated with growth factors for 4 and 24 h. Main images are representative regions from the insets. Scale bars: 5 µm.
