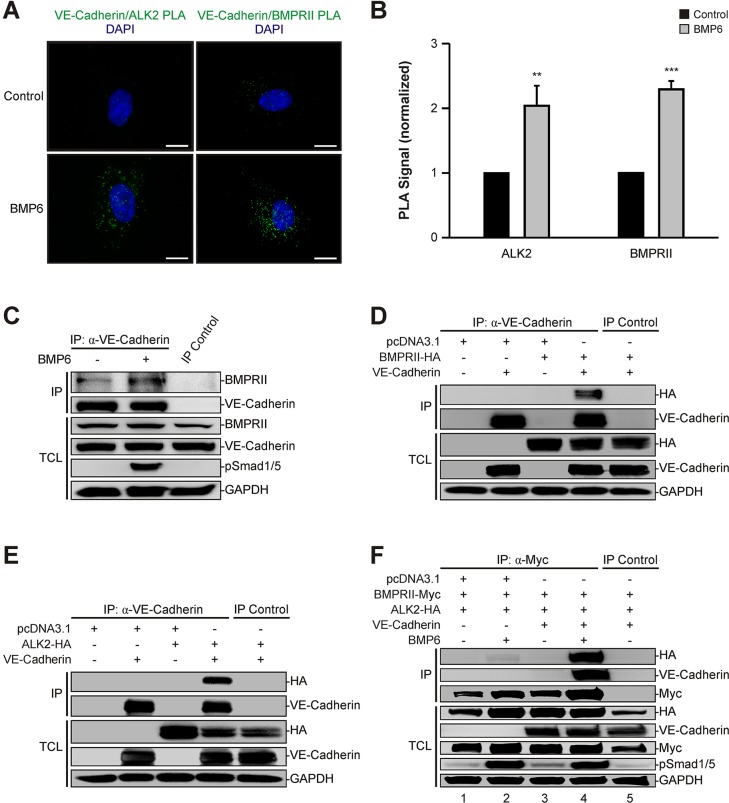
Fig. 5.
VE-cadherin interacts with BMP receptors. (A) In situ proximity ligation assay (PLA) of VE-cadherin and the BMP receptors ALK2 and BMPRII. HUVECs were treated with BMP6 for 60 min and association of VE-cadherin and ALK2 or BMPRII was visualized using an in situ PLA (green). DAPI, blue. Scale bars: 10 µm. (B) Quantitation of VE-cadherin–ALK2 and VE-cadherin–BMPRII heteromers shown in A. Mean±s.d. from three independent experiments. (C) VE-cadherin interacts endogenously with BMPRII. VE-cadherin was immunoprecipitated with a VE-cadherin-specific antibody from confluent HUVECs stimulated with BMP6 for 60 min and samples were blotted as indicated. Recombinant protein A-Sepharose beads served as an IP control. TCLs represent lysates not subjected to immunoprecipitation. (D) VE-cadherin associates with BMPRII upon overexpression. HEK293T cells were transfected with VE-cadherin and BMPRII-HA, and VE-cadherin was immunoprecipitated with a VE-cadherin-specific antibody. Normal IgG antibody served as IP control. (E) VE-cadherin associates with ALK2 upon overexpression. HEK293T cells were transfected with VE-cadherin and ALK2-HA, and VE-cadherin was immunoprecipitated with a VE-cadherin-specific antibody. Normal IgG antibody served as IP control. (F) VE-cadherin facilitates BMP receptor complex formation. HEK293T cells were transfected with BMPRII-Myc and ALK2-HA in the absence or presence of co-expressed VE-cadherin. Cells were stimulated with BMP6 for 45 min, followed by immunoprecipitation of Myc-tagged BMPRII with a Myc-specific antibody. Mouse IgG isotype antibody served as IP control. **P≤0.005, ***P≤0.001.