Figure 1. Sequence, Structure and Pairing Alignments of the 3’,3’-cGAMP Riboswitch with bound 3’,3’-cGAMP.
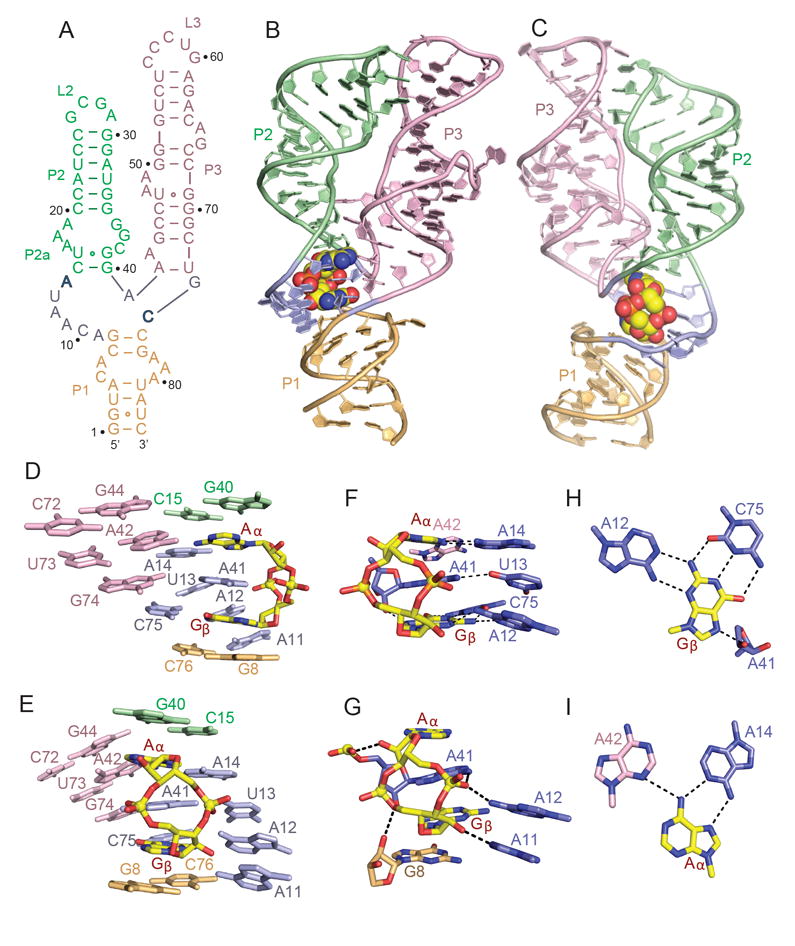
(A) Schematic of the secondary structure of the Gs1761 3’,3’-cGAMP riboswitch. This sequence differs from the natural riboswitch by containing A2G, U72C and C73U substitutions.
(B, C) Two alternate views of the 2.05 A structure of the 3’,3’-cGAMP riboswitch with bound 3’,3’-cGAMP. The riboswitch RNA is shown in a ribbon representation and color coded by segments, while the bound 3’,3’-cGAMP is shown in a space-filling representation. Residues A14 and C74 that interact through base pairing with the bound cGAMP are shown in bold.
(D, E) Two alternate views showing base stacking alignments within the 3’,3’-c-GAMP riboswitch (color-coded) centered about the bound 3’,3’-cGAMP (in yellow).
(F, G) Two alternate views showing intermolecular base-base (panel F) and base-sugar-phosphate (panel G) hydrogen bonding interactions between 3’,3’-cGAMP (in yellow) and the riboswitch RNA residues (color-coded) centered about the binding site in the complex.
(H) Intermolecular recognition of Gβ of 3’,3’-cGAMP (in yellow) by base-base hydrogen bonding with riboswitch RNA bases (in blue) in the complex.
(I) Intermolecular recognition of Aα of 3’,3’-cGAMP (in yellow) by base-base hydrogen bonding with riboswitch RNA bases (color-coded) in the complex. See also Table S1 and Figure S1.
