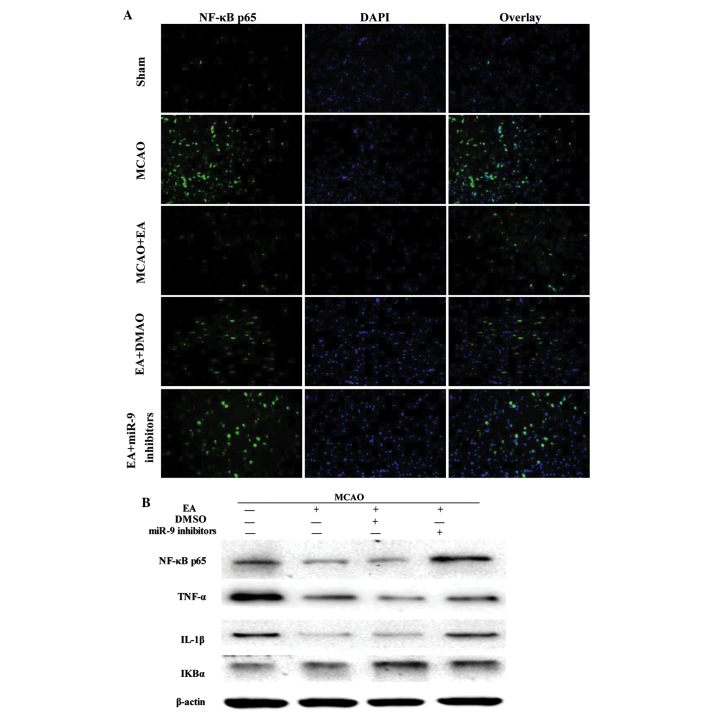
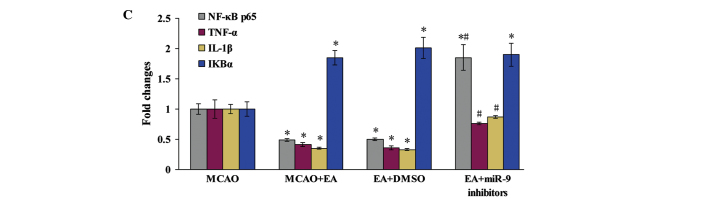
Figure 4.
Effect of EA on NF-κB signaling pathway-associated factors. (A) Evaluation of NF-κB p65 (green), DAPI (blue) and the colocalization positive cells in peri-infarct cortical tissue of the Sham, MCAO, MCAO + EA, EA + DMSO and EA + miR-9 inhibitor groups (n=4). (B) Western blot analysis of the protein expression levels of NF-κB p65, TNF-α, IL-1β and IκBα in the peri-infarct cortical tissue of the MCAO, MCAO + EA, EA + DMSO and EA + miR-9 inhibitors groups. (C) Bar graph showing the fold change of NF-κB p65, TNF-α, IL-1β and IκBα in each group (n=4) (*P<0.05, vs. MCAO group; #P<0.05, vs. MCAO + EA and EA + DMSO groups). EA, electroacupuncture; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; miR-9, microRNA-9; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IκBα, inhibitor of κBα.