Figure 1.
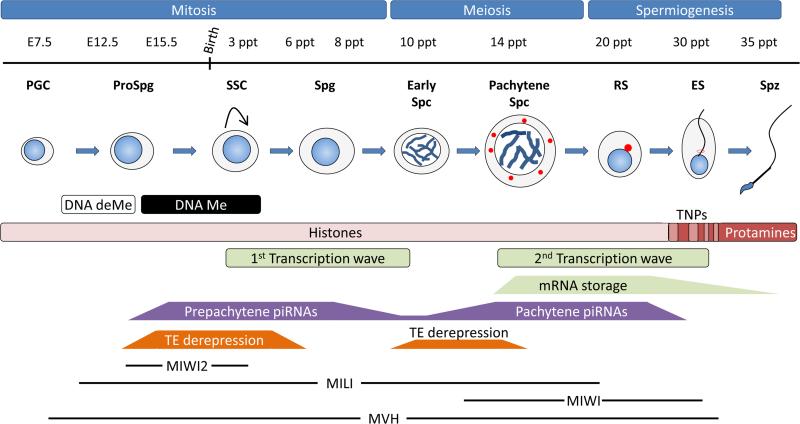
Spermatogenic process in the mouse testis. During embryogenesis primordial germ cells (PGCs) are specified at embryonic day E7.5. They proliferate and migrate to the future gonads at E11.5 and become arrested at G1 as prospermatogonia (ProSpg). During this phase, a genome-wide epigenetic reprogramming occurs in embryonic germ cells through the near to complete erasure of somatic DNA methylation patterns (DNA deMe) followed by the acquisition of novel sex-specific DNA methylation including differential imprinting of the genes in the male and female germ cells (DNA Me). After birth, the Spermatogonial Stem Cell (SSC) divide mitotically to generate more spermatogonia (Spg) or to differentiate into primary spermatocytes. Early spermatocytes (Early Spc) will enter into meiosis during which synaptonemal complex formation, crossing over and homologous recombination take place in the Pachytene spermatocyte (Pachytene Spc). Round spermatids (RS) are the first haploid cells and undergo a differentiation process or spermiogenesis where elongating spermatids (ES) have their histones replaced first by transition proteins and finally by protamines in the spermatozoa (Spz). Two extensive wave of transcription occurs before and after meiosis and the second lead to the storage of mRNAs that will be needed in the last stages of the spermatogenesis when transcriptions ceases. Unlike Pachytene piRNAs, Prepachytene piRNAs are enriched in sequences that match transposable elements (TEs) and both are expressed at specific spermatogenic stages. Prepachytene piRNAs are expressed simultaneously with MIWI2 (from E15.5 until soon after birth) and MILI (from E12.5 to RS) in foetal ProSpg and during this period there is an extensive derepression of transposable elements (TE) that also occurs in early meiotic spermatocytes. Pachytene piRNAs are expressed together with MIWI (from pachytene Spc until RS) and the presence of the CB (red dots). The MVH, a hallmark of the CB, is exclusively expressed in male germ cells from E10.5 to RS and has been proposed to be involved in both miRNA and piRNA pathways.