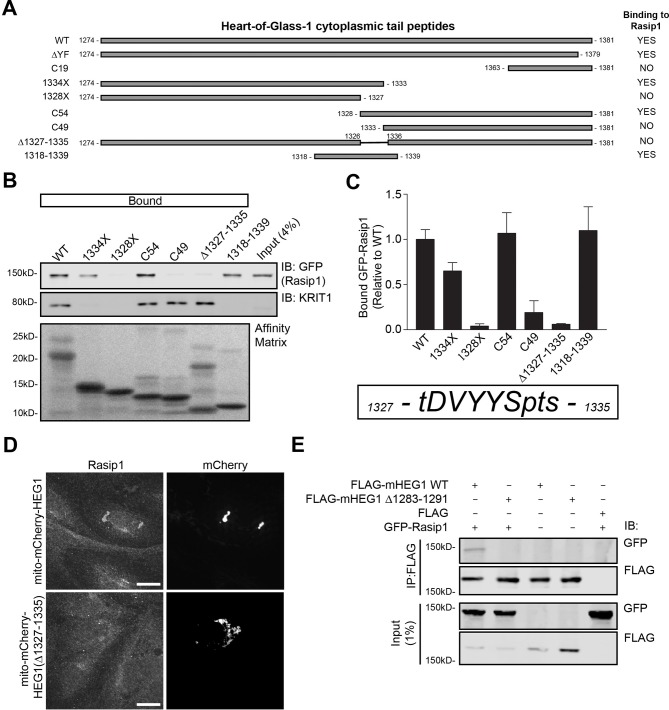
Figure 4. Rasip1 binds to HEG1 upstream of the KRIT1-binding site.
(A) Schematic representation of different HEG1 cytoplasmic tail peptides used to map the binding region for Rasip1. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP-tagged full-length Rasip1. Western blot analysis shows that HEG1 wild-type (WT), 1334X, C54, and 1318-1339 bound to GFP-Rasip1. In contrast, HEG1 1328X, C49, and ∆1327-1335 failed to bind to GFP-Rasip1. Endogenous KRIT1 binding was only observed for HEG1 WT, C54, C49, and ∆1327-1335 which al contain the C-terminal YF motif. Affinity Matrix was visualized by Ponceau staining. (C) Top section: Bar diagram shows binding of GFP-Rasip1 to HEG1 cytoplasmic tail peptides relative to wild-type HEG1. Mean values ± SEM are shown from at least 3 independent experiments. Bottom section: HEG1 1327-1335 (TDVYYSPTS) is necessary for Rasip1 binding. (D) HUVECs, transfected with mito-mCherry-HEG1 or mito-mCherry-HEG1(∆1327-1335), were analyzed by Spinning Disk Confocal Miroscopy (SDCM) for endogenous Rasip1 localization. A fraction of Rasip1 was targeted to mito-mCherry-HEG1 positive structures but not to mito-mCherry-HEG1(∆1327-1335). Scale bars, 10 µm. (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP-tagged full-length Rasip1, FLAG-tagged murine HEG1 full-length, ∆1283-1291 (corresponding to aa 1327-–1335 in human HEG1), empty vector, or both. Immunoprecipitation was done by using anti-FLAG G1 resin and bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blot analysis shows that GFP-tagged Rasip1 was co-immunoprecipitated with full-length mHEG1 but not mHEG1(∆1283-–1291).