Figure 2.
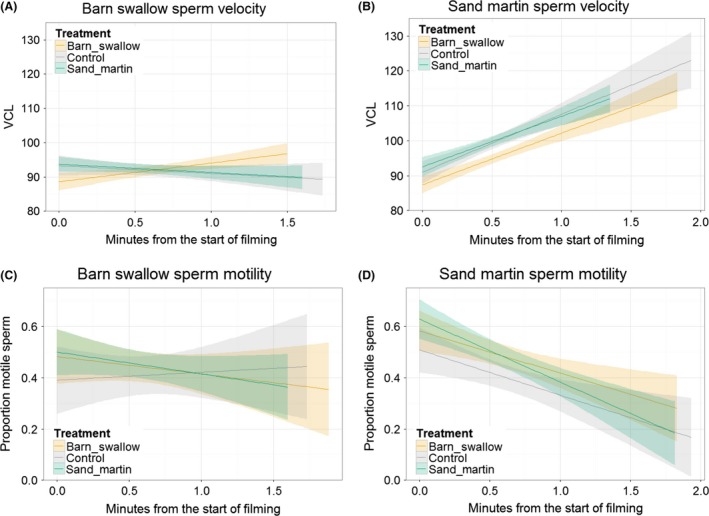
Change in sperm swimming parameters (A, B: sperm velocity, VCL, μm/S; C, D: proportion of motile sperm) over time in barn swallows (A, C) and sand martins (B, D). Sperm were mixed with fluid from the reproductive tract of barn swallow females (tan), sand martin females (blue) or a control saline solution (gray) before being filmed. (A, B) Sand martin sperm swimming speed increased over time more than did barn swallow sperm swimming speed, and barn swallow female fluid supported a faster increase in sperm swimming speed for males of both species. (C, D) The proportion of motile cells decreased over time, and was lower in the control treatment than in female fluids, for both male species. Decrease over time was faster in sand martin ejaculates than in barn swallow ejaculates. Plots drawn using ggplot2 using raw data; shading indicates 95% confidence intervals; statistical tests were performed with both male species considered simultaneously, although they are drawn separately here.
