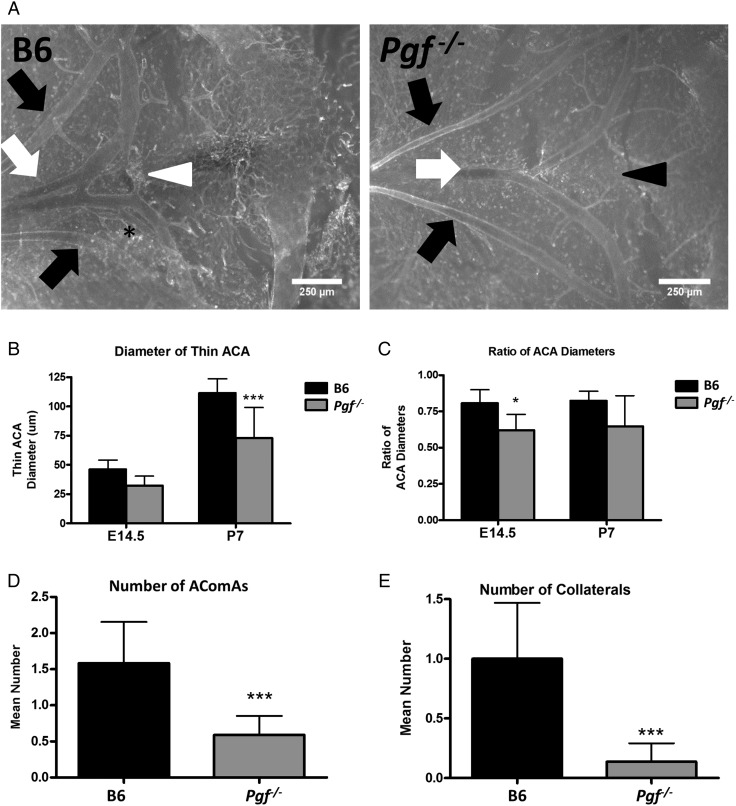
Figure 5.
Whole mount vascular staining of circle of Willis (cW) at embryonic day (E) 14.5 and post-natal day (P) 7. Whole mount immunofluorescence with isolectin B4 (IB4; white) provided visualization of the anterior cerebral arteries (ACAs: white arrows), olfactory arteries (black arrows) and the anterior communicating artery (AComA; white arrowhead) in B6 and Pgf −/− brains at E14.5 (A) and P7 (not shown). In many B6 brains, an extra vessel along the ACA was present (asterisk) while in some Pgf −/− brains, the AComA was absent (black arrowhead). Significant changes in the Pgf −/− cW included a narrower diameter of one ACA (B) but not both ACAs, resulting in a decreased ratio of the ACA diameters (C). The number of vessels present in the anterior cW of Pgf −/− mice was fewer than in B6 mice. The mean number of AComAs in the Pgf −/− cW at E14.5 was fewer than in B6 (D). Similarly, at E14.5, the mean number of collateral vessels in the Pgf −/−cW was reduced (E). Means with 95% confidence intervals are shown with P < 0.05, P < 0.01, and P < 0.001 represented by *, **, and *** respectively.