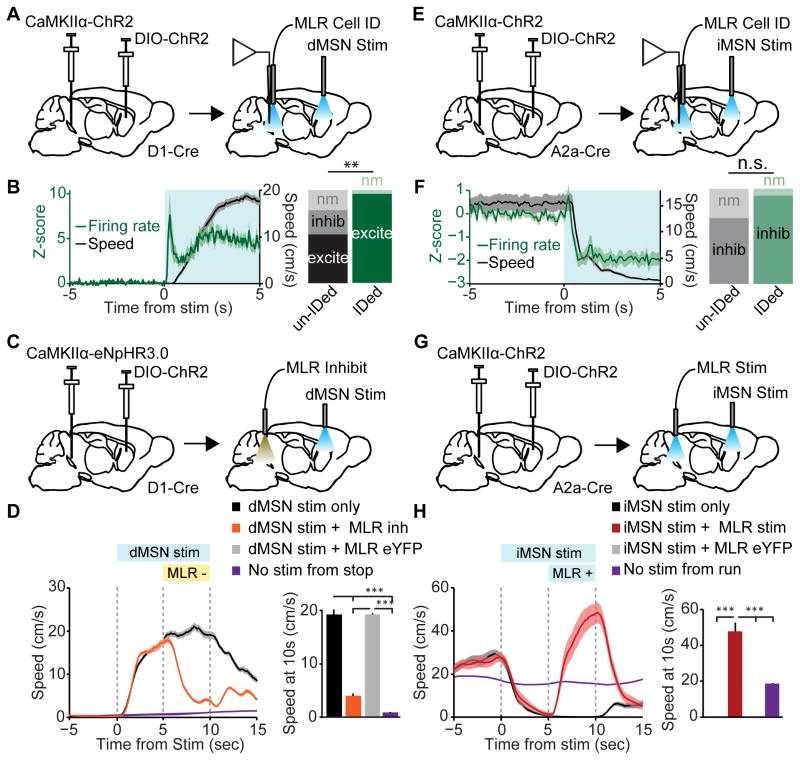
Figure 6. MLR glutamatergic neurons are necessary and sufficient to reverse the effects of BG stimulation.
(A) Schematic for recording MLR glutamatergic neurons, while activating dMSNs in striatum. (B) Left, Z-scored firing rate of identified glutamatergic neurons (green line, left axis) and speed (black line, right axis) aligned to onset of 5 second unilateral dMSN stimulation from stop. Right, fractions of excited (excite), inhibited (inhib), or non-modulated (nm) units in unidentified recordings (un-IDed, left) and in identified glutamatergic cells (IDed, right). (identified: 25 excited, 0 inhibited, 1 non-modulated from 4 mice; unidentified: 22 excited, 11 inhibited, 9 non-modulated from 4 mice; ** p < 0.001, χ2 test). (C) Schematic for stimulating dMSNs in striatum, while inhibiting MLR glutamatergic neurons. (D) Left, Speed aligned to unilateral dMSN stimulation. Orange line, trials in which green light was turned on in the MLR 5 seconds after dMSN stimulation; black line, interleaved trials in which green light was omitted; purple line, no stimulation trials when mouse is stopped. Right, Speed 10 seconds after onset of dMSN stimulation (*** p < 10−4, Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA, χ23,136 = 92.35, p < 10−10, with Dunn-Sidak post test). (E) Schematic for recording identified MLR glutamatergic neurons, while activating iMSNs in striatum. (F) Left, Z-scored firing rate of glutamatergic neurons (green line, left axis) and speed (black line, right axis) aligned to onset of 5 second bilateral iMSN stimulation from running. Right, summaries for the number of inhibited (inhib) or non-modulated (nm) units in unidentified (unIDed, left) recordings and identified (IDed, right) glutamatergic neurons (identified: 25 inhibited, 2 unmodulated from 4 mice; unidentified: 18 inhibited, 8 unmodulated from 3 mice; p = 0.09, χ2 test). (G) Schematic for stimulating iMSNs in striatum while stimulating glutamatergic cells in the MLR. (H) Left, time course of mouse speed aligned to bilateral iMSN stimulation. Red line, trials in which blue light was turned on in the MLR at 20 Hz 5 seconds after iMSN stimulation; black line, interleaved trials in which green light was omitted; purple line, no stimulation trials when mouse is running. Right, summary of mouse speed 10 seconds after onset of iMSN stimulation (*** p < 10−4 , Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA, χ23,105 = 75.06, p < 10−10, with Dunn-Sidak post test). Shaded regions, s.e.m. See also Figures S5 and S6.