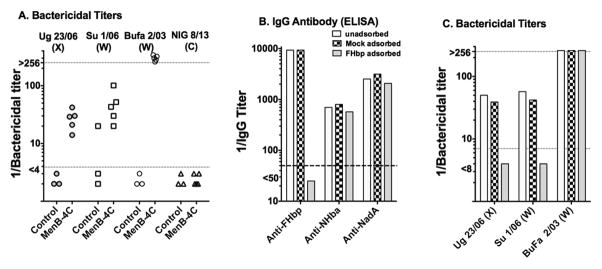
Figure 4. Effect of depletion of anti-FHbp antibodies on serum bactericidal antibody responses of infant macaques immunized with MenB-4C.
Panel A. Serum bactericidal titers of five infant macaques immunized in a previous study with two doses of MenB-4C [25] measured in the present study against four representative African serogroup X, W or C strains. The macaque FH in all five animals bound strongly to FHbp. Control macaques are unvaccinated animals of the same ages as the vaccinated animals. Each symbol represents the serum titer of an individual animal. Strains Ug23/06, SU 1/06 and NIG 8/13 were resistant to serum bactericidal activity elicited in human FH transgenic mice immunized with the MenB-4C vaccine, and strain BuFa 2/03 was susceptible. The resistant serogroup C strain, NIG 8/13, was killed by a positive control anticapsular mAb. Panel B. Adequacy of depletion of anti-FHbp antibodies in previously described [41] adsorbed and unadsorbed serum pools from the five MenB-4C-vaccinated animals as measured by ELISA. Panel C. Effect of depletion of anti-FHbp on bactericidal activity measured in the present study against three of the African strains. The bars represent the titers of the unadsorbed and adsorbed pooled serums. Each of the strains expresses NHba; strains Su 1/06 and BuFa 2/03 also have moderate and high NadA expression, respectively (Supplemental Figure S2). Strains BuFa 2/03 and NIG 8/13 have FHbp sub-family A and strains Ug 23/06 and Su 1/06 have FHbp sub-family B (Table 1).