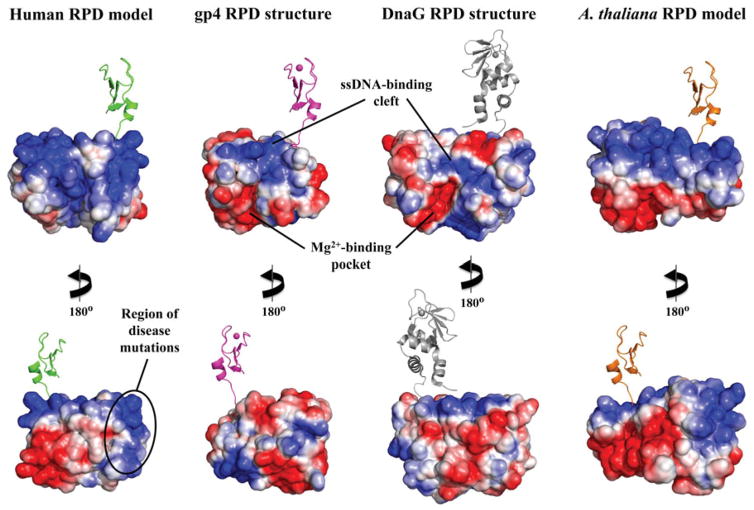
Figure 5.
Electrostatic potential surface (EPS) map suggests a new DNA-binding region for the RPD of human mtDNA helicase. EPS maps for the RPD structures of T7 gp4 (residues 64–255, 1NUI), E. coli DnaG (residues 115–366, 1DDE) and the mtDNA helicase models of humans (residues 153–362) and Arabidopsis thaliana (residues 191–408) were calculated using the APBS Tools built into Pymol, with default settings. The solvent accessible surfaces shown are colored according to electrostatic potential (blue≥+10 kT, red≤−10 kT). The ZBD is depicted in cartoon representation to provide a reference for the N-terminal region of these enzymes. The human and A. thaliana ZBD representations are copies of the same domain from T7 gp4 and are positioned as if they provide the same structural arrangements and function as in the bacteriophage enzyme; they are not meant, however, to depict any structural similarities between the ZBDs of mtDNA helicases and the T7 primase–helicase. The bacterial ZBD was retrieved from the crystal structure of the Aquifex aeolicus DnaG (PDB: 2AU3) (see color version of this figure at www.informahealthcare.com/bmg).