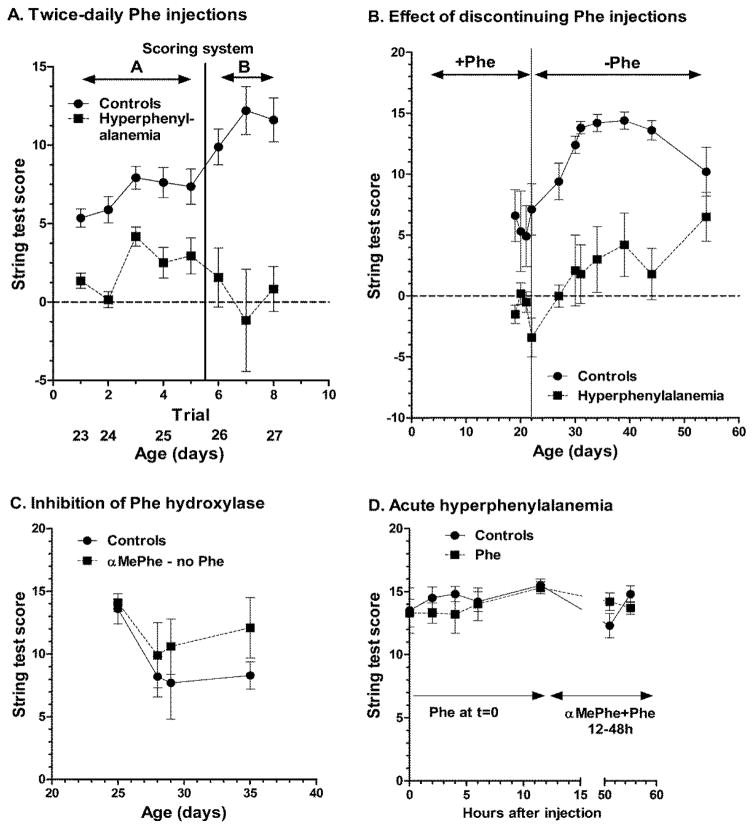
Fig. 4. Behavioral testing of hyperphenylalanemic rats.
(A) Rats were given daily injections of 0.9% NaCl or α-methylphenylalanine (αMePhe, 2.4 μmol/g) + phenylalanine (Phe, 5.2 μmol/g) plus a second injection 10–12h later of only Phe (2.6 μmol/g) or NaCl from age 3 to 27 days. Rats were weaned at age 21 days. Twice-daily string tests were initiated at age 23 days; the odd-numbered trials were carried out at 6h after the NaCl or α-MePhe+Phe injection when brain Phe concentrations would be highest (see Fig. 1), and subsequent even numbered trials at ages 24–26 days were carried out at 12h after the NaCl or α-MePhe+Phe injection (just prior to the second Phe injection) when brain Phe level would be lower. Scoring system A (see below) was used for trials 1–5 and scoring system B was used for trials 6–8 (n = 13 controls and n = 6–13 hyperphenylalanemic rats). These rats were then used to determine CMRglc (Fig. 3). (B) Rats were given daily injections as described above from age 3–22 days, then the injections were terminated. Once-daily string tests using scoring system B were carried out from age 19–54 days (n=5 controls and 4–5 hyperphenylalanemic rats). (C) Rats were given single daily injections from age 3 to 35 days of 0.9% NaCl (n = 5) or αMePhe (2.4 μmol/g; n = 7) and string tests scored with system B were carried out at intervals beginning on day 25. (D) Rats were given a single injection of 0.9% NaCl (n=6) or phenylalanine (Phe, 5.2 μmol/g; n = 6) at age 31 days and string tests scored with system B were carried out at timed intervals. At 12 and 24h after the last string test, the rats were given αMePhe (2.4 μmol/g) + Phe (5.2 μmol/g), followed by Phe (5.2 μmol/g) at 36, and αMePhe (2.4 μmol/g) + Phe (5.2 μmol/g) at 48h; string tests carried out at 3h and 7h after the last injection. The major difference between the scoring systems A and B is that system B gives more points for rapid movement along the string to the platform and penalizes hanging in place; these changes increase behavioral discrimination between the control and experimental rats. Scoring systems A and B, respectively, allocated points as follows, where dashes indicate a characteristic that was not included in the scoring system: each paw kept on string for ≥5s (1 point, 1 point); tail kept on string for 5s (2, 2); continuous travel along string for each ≥5s of travel (3,3); reaching one of vertical poles (2, -) within 0–5s (-, 16), 5–15s (-, 7), 16–30s (-, 4), or 31–60s (-, 2); falling off string within 0–15s (−3, −3), 16–30s (−2, −2), or 31–60s (−1, −1); penalties for each occurrence of hanging motionless for 5s (−3, −3) or hanging in place without moving paws from their position on the string (-, −2). Values are means ± SEM. Rats in all experimental groups were weaned at age 21 days. The string test scores for the hyperphenylalanemic rats were significantly lower than controls in panels A and B (P<0.001, 2-way ANOVA), whereas there were no significant differences among the groups in panels C and D. Body weights at 23, 25, and 27 days, respectively, were 48.7 ± 1.1, 57.8 ± 1.3, and 69.4 ± 1.4 g for controls and 40.6 ± 1.8, 46.9 ± 2.0, and 51.6 ± 0.5 g for hyperphenylalanemic rats; weights of the Phe-treated rats were significantly less than controls at all ages (P<0.001, 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni multiple comparisons test).