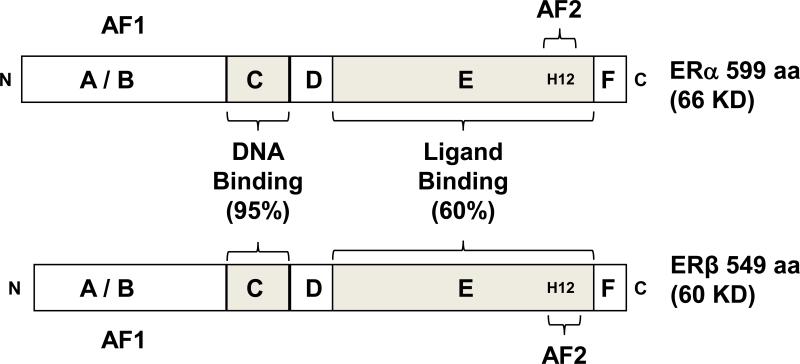
Figure 1.
Structures of ERα and ERβ protein with functional domains. Estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ share a conserved domain structure. The A/B domain, at the amino terminus (N) of the protein contains activation function 1 (AF1). The C domain binds to DNA motifs called estrogen responsive elements (EREs). The D domain is called the hinge region, and contributes to DNA binding specificity and nuclear localization of the ERs. The E domain is called the ligand binding domain because it interacts with estrogen, through an arrangement of 11 α helices (H1, and H3 through H12). H12 in this region of the receptor is critical to mediating transcriptional activation via activation function 2 (AF2). At the carboxy terminus (C) is the F domain. The % homology shared between ERα and ERβ in the C and E domains is shown.