Figure 6.
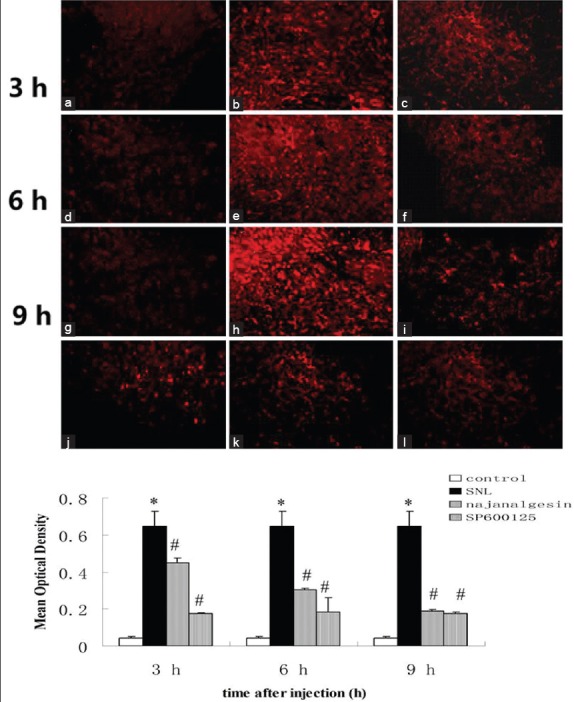
Changes in c-Jun N-terminal kinase protein expression in the spinal dorsal horn after L5 spinal nerve ligation, transection-induced neuropathic pain, and najanalgesin treatment. Images show c-Jun N-terminal kinase immunostaining in the spinal dorsal horn in the control, spinal nerve ligation, najanalgesin treatment, and SP600125 treatment groups. Lower magnification images showing the area of the dorsal horn that was analyzed. c-Jun N-terminal kinase-IR activation was not observed in the control group (a, d, g). Prominent astrocyte activation was observed in rats treated with intrathecal saline after spinal nerve ligation (b, e, h). These responses were markedly inhibited in rats treated with either intrathecal najanalgesin (c, f, i) or intrathecal SP600125 (j, k, l) for 3, 6, and 9 h. The c-Jun N-terminal kinase protein expression at all of the investigated time points was quantified and graphed. (a-i) ×200. The data are represented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. (n = 6). *P < 0.05 versus the control group; #P < 0.05 versus the spinal nerve ligation group.
