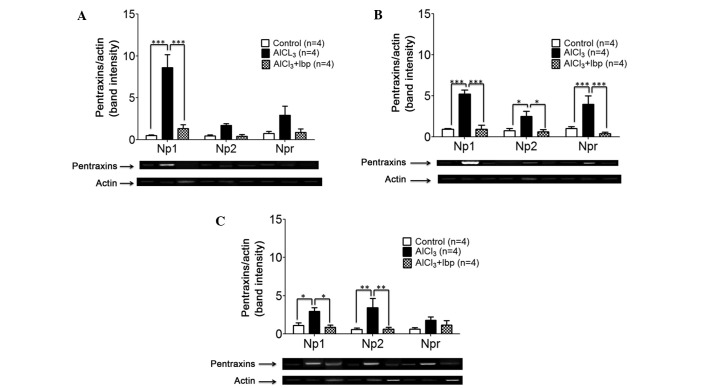
Figure 3.
Effects of ibuprofen treatment on the expression levels of neuronal pentraxins in the various brain structures of an AlCl3-induced mouse model of neurotoxicity. (A) Ibuprofen treatment significantly decreased the expression levels of NP1 in the hippocampus, as compared with the AlCl3-treated group. (B) Ibuprofen significantly decreased the expression levels of NP1, NP2 and NPR in the cortex, as compared with the AlCl3-treated group. (C) Ibuprofen significantly decreased the expression levels of NP1 and NP2 in the amygdala, as compared with the AlCl3-treated group. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and agarose gel electrophoresis were used to analyze the expression levels of NP1, NP2 and NPR in the various brain compartments. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n=4). *P<0.05 vs. the AlCl3-treated group; **P<0.01 vs. the AlCl3-treated group; ***P<0.001 vs. the AlCl3-treated group. NP1, neuronal pentraxin-1; NP2, neuronal pentraxin-2; NPR, neuronal pentraxin receptor; Ibp, ibuprofen; AlCl3, aluminum chloride.