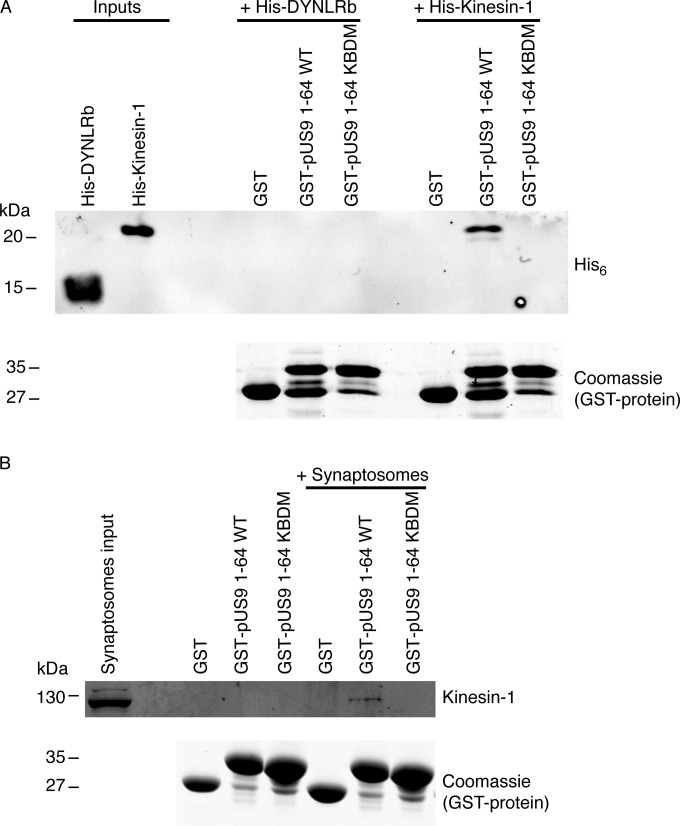
FIG 4.
Confirmation that the pUS9 kinesin binding domain (KBD) is essential for binding kinesin-1. (A and B) In vitro pulldown assay was undertaken with a GST-tagged HSV-1 pUS9 cytoplasmic tail (residues 1 to 64) containing a substitution mutation. This mutation, KBDM, consisted of pUS9 residues 57 to 61 with the sequence RRRRR mutated to NNNNN. Binding of either the His6-tagged kinesin-1 C-terminal domain (A) or native kinesin-1 (derived from rat brain synaptosomes) (B) was abolished for the GST-tagged pUS9 KBDM but not the GST-tagged pUS9 WT. This also illustrates that HSV-1 pUS9 binds native kinesin-1. The upper images in each case are immunoblots (anti-His6 tag [A] or anti-kinesin-1 [B]) to detect either His6-tagged proteins or kinesin-1 eluted from boiled GST Bind beads. The lower images in panels A and B are total protein stains with Coomassie blue to confirm the presence of GST-tagged proteins eluted from Bind GST Bind beads.