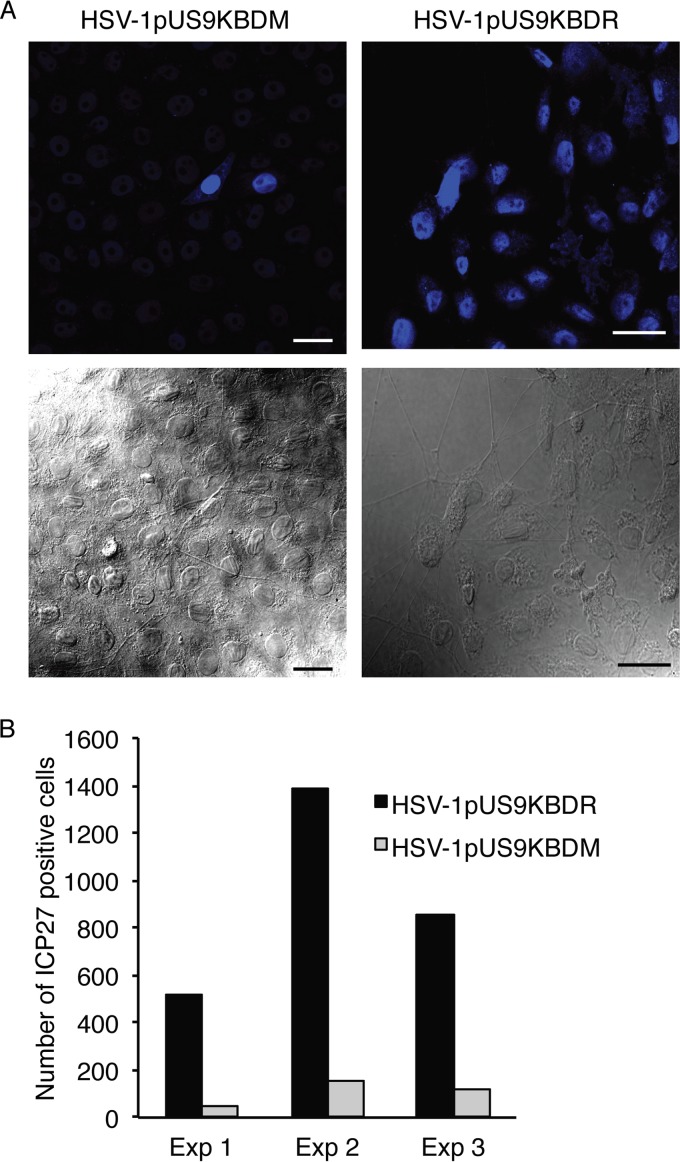
FIG 8.
HSV-1 spread from axons to nonneuronal Vero cells. Neonatal rat DRG neurons were dissociated, pelleted through a 35% Percoll gradient, and plated into the somal compartment of three-chamber microfluidic devices. Cultures were incubated for 5 to 6 days to allow axons to grow in the axonal compartment. Vero cells were added to the axonal compartment 24 h prior to addition of either HSV-1pUS9KBDM or HSV-1pUS9KBDR (5 PFU/cell) to the somal compartment. Foscarnet (100 μg/ml) was added to the axonal compartment 8 h p.i. to prevent secondary virus spread in Vero cells. The cultures were fixed at 22 h p.i., immunostained for HSV-1 immediate-early protein ICP27, and examined using a Leica SP5 confocal microscope. (A) Representative confocal micrographs of Vero cells in the axonal compartment. (Lower) The presence of axons innervating the Vero cells was confirmed for each virus. (Upper) Vero cells were counted from 10 randomly selected fields of view and scored as positive or negative for the presence of HSV-1 ICP27 (blue). Scale bars, 25 μm. (B) The total number of ICP27-positive Vero cells in the axonal compartment was counted for each virus in three separate experiments (Exp). A significant reduction in virus spread from axons to Vero cells was observed for HSV-1pUS9KBDM compared to that of HSV-1pUS9KBDR.