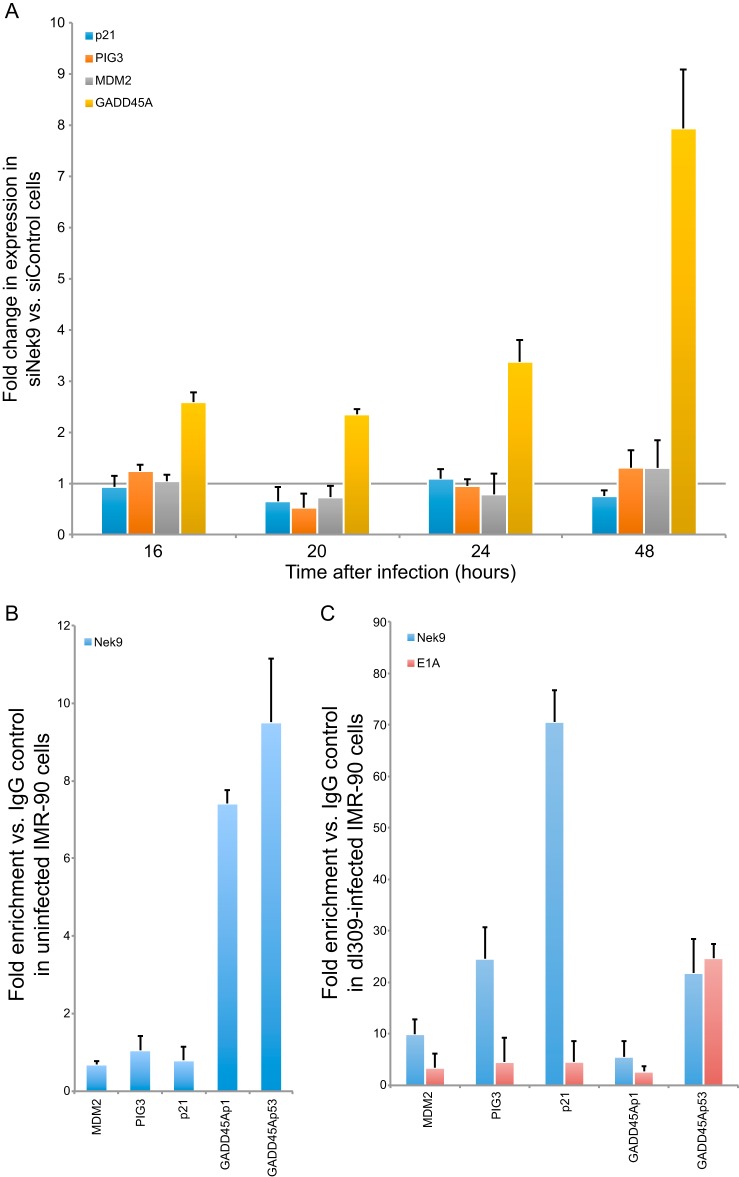
FIG 8.
Nek9 affects GADD45A expression during viral infection and is recruited to the intronic, p53-regulated GADD45A promoter. (A) IMR-90 cells that were transfected with siRNAs, either siControl as a control or siNek9 to deplete Nek9, were infected with dl309 24 h after knockdown at an MOI of 5. Cellular gene expression was monitored by RT-qPCR at the indicated time. GAPDH mRNA was used as the normalization control. Note that these are the same samples as in Fig. 2A. n = 4; error bars represent SD. (B) ChIP was carried out on uninfected and subconfluent IMR-90 cells using the Nek9 antibody as described in Materials and Methods. Data are represented as fold enrichment versus IgG negative control (12CA5 monoclonal antibody). Occupancy was analyzed for Nek9 at the MDM2, PIG3, p21, GADD45Ap1 (not bound by p53), and GADD45Ap53 (bound by p53) promoters. n = 3; error bars represent SD. (C) IMR-90 cells were infected with dl309 at an MOI of 5, and ChIP was performed 24 h after infection using E1A or Nek9 antibodies as indicated and as described in Materials and Methods. Data are represented as fold enrichment versus IgG negative control (12CA5 monoclonal antibody). Occupancy was analyzed for Nek9 and E1A at the MDM2, PIG3, p21, GADD45Ap1, and GADD45Ap53 promoters. n = 3; error bars represent SD.