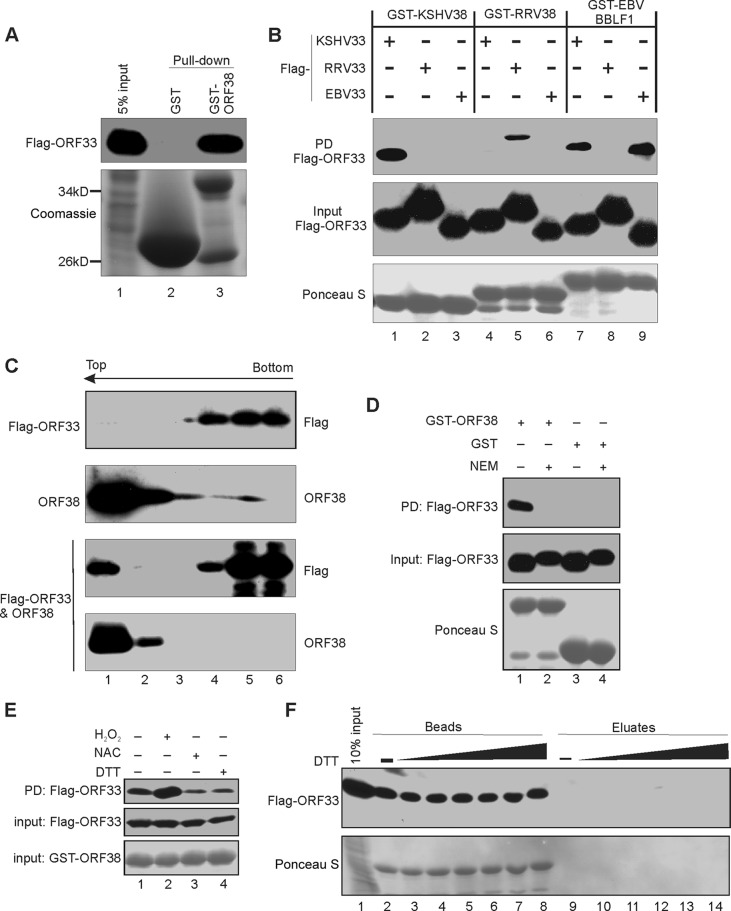
FIG 2.
Interaction between ORF33 and ORF38. (A) GST-ORF38 interacts with ORF33. GST or GST-ORF38 was used to pull down cell lysates expressing Flag-ORF33, and the input/eluates were probed with anti-FLAG antibody. (B) Interactions between ORF33 and ORF38 homologues. GST-ORF38 proteins were used to pull down (PD) lysates of HEK293T cells expressing different Flag-ORF33 homologs. The inputs/eluates were probed with the indicated antibodies. (C) ORF33 and ORF38 interact in cells. Lysates of HEK293T cells transiently expressing Flag-ORF33 and/or ORF38 were subjected to a membrane flotation assay as described in Materials and Methods. Six fractions were collected and analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. Representative blots of our three replicates are shown. (D) The effect of N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) on GST-ORF38–ORF33 interaction. GST-ORF38 was used to pull down lysates of HEK293T cells expressing Flag-ORF33 that were pretreated with NEM or not pretreated. The input/eluates were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (E) The interaction between ORF33 and ORF38 occurred preferentially in oxidized environments. The pulldown was performed as described for panel D, except that cells were pretreated with H2O2, NAC, or DTT as described in Materials and Methods. (F) The interaction between GST-ORF38 and ORF33 is not mediated by disulfide bond formation. The complex of GST-ORF38 with Flag-ORF33 was treated with increasing concentrations of DTT. The proteins released into the eluate or retained on the beads were analyzed by Western blotting.