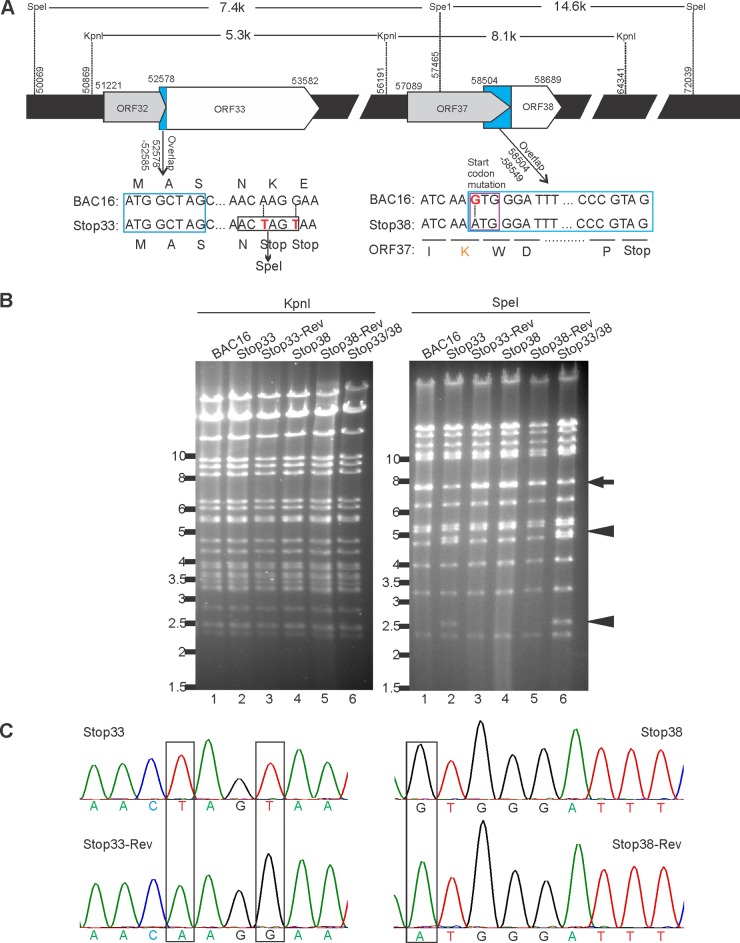
FIG 3.
Construction of ORF33-null, ORF38-null, and ORF33/ORF38-null mutants in BAC16. (A) Schematic diagram of ORF33-null or ORF38-null mutant constructions. For the ORF33 mutant, the 14th and 15th codons (AAG and GAA) were changed to two consecutive stop codons (TAG and TAA), thereby introducing a new restriction enzyme site (SpeI). For the ORF38 mutant, the start codon ATG was mutated to GTG. This modification resulted in the replacement of ORF37 codon AAA with AAG, both of which code for lysine. The blue box indicates overlap sequences. The indicated base pair number is derived from the previously annotated BAC16-GFP sequence (37). (B) RFLP analysis of wild-type and mutant BACs. Electrophoresis of KpnI- or SpeI-digested wild-type, mutant, and revertant BAC16 DNAs is shown. The arrow indicates the wild-type pattern, while the arrowheads indicate the predicted changes as a consequence of the newly introduced SpeI site in the ORF33 mutant. (C) Sequences of the wild type, mutants, and revertants in the ORF33 or ORF38 loci. The sequence chromatographs are shown, and the predicted mutations are boxed.