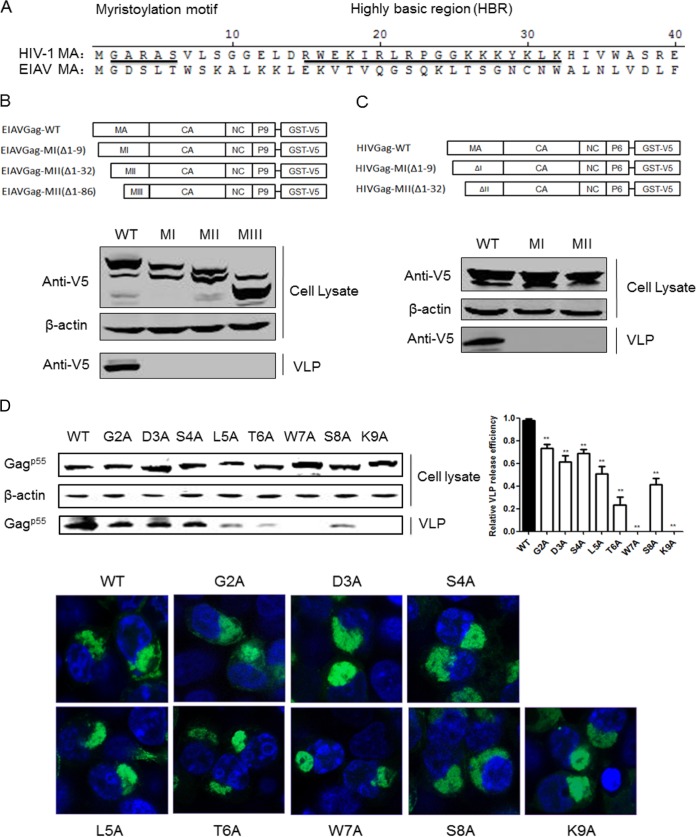
FIG 2.
The N terminus of EIAV and HIV-1 MA was essential for Gag assembly. (A) Comparison of N-terminal amino acid sequences in MAs from EIAV and HIV-1. The myristoylation motif and the highly basic region (HBR) are underlined and indicated in HIV-1 MA sequences. (B and C) 293T cells were transfected with the truncated EIAV and HIV-1 Gag constructs. After 48 h, the cells were lysed, and Gag VLPs in the supernatant were purified by centrifugation at 20,000 × g for 2 h at 4°C. Gag proteins in the cell lysate and supernatant were detected using anti-V5 antibodies. Cell lysates were also analyzed for equal amounts of total proteins using the anti-β-actin monoclonal antibody. (D) All EIAV Gag mutants were fused with GFP in the C terminus and transfected into 293T cells. Gag expression and release were detected with anti-GFP antibodies. The relative virus release efficiency was calculated as the amount of VLP-associated Gag as a fraction of the total Gag present in the cell and VLP lysates and normalized to the virus release efficiency in wild-type group. Additionally, the cellular distribution of the mutants was analyzed by confocal microscope. **, P < 0.005.