Figure 2. Association (odds ratio and 95% confidence intervals) between randomization, discipline and type of intervention (surgical/non-surgical).
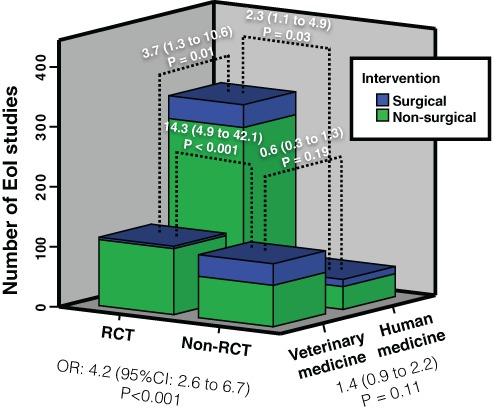
Notice that the overall prevalence of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and prevalence of surgical RCTs were lower in veterinary medicine (ORs: 4.2 and 3.7, respectively). However, surgical interventions were more likely to be non-randomized in both disciplines (ORs: 14.3 and 2.3).
