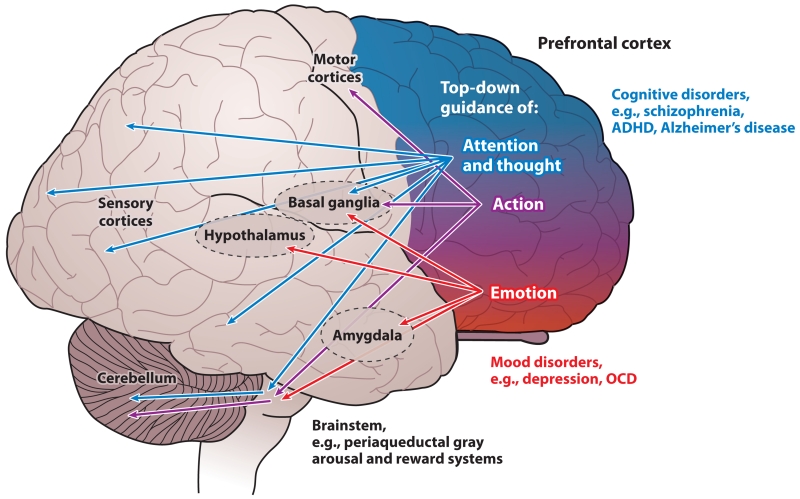
Figure 1.
Topographic organization of PFC functions in primates. The primate PFC provides top-down guidance of attention and thought (blue), action (purple), and emotion (red) through its extensive projections. In general, the PFC is organized topographically, with dorsal and lateral regions regulating thought and attention and ventral and medial regions regulating emotion. This organization is reflected in the PFC projections through the basal ganglia via the dorsal and ventral striatum. There are also parallel projections to the cerebellum via the pontine nuclei. The human brain is lateralized, with the left hemisphere specialized for language and the right hemisphere specialized for inhibition of inappropriate thoughts, actions, and emotions. Dysfunction of the dorsal and lateral PFC is associated with cognitive disorders, whereas more ventral and medial areas are altered in affective disorders. Abbreviations: ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; OCD, obsessive-compulsive disorder; PFC, prefrontal cortex.