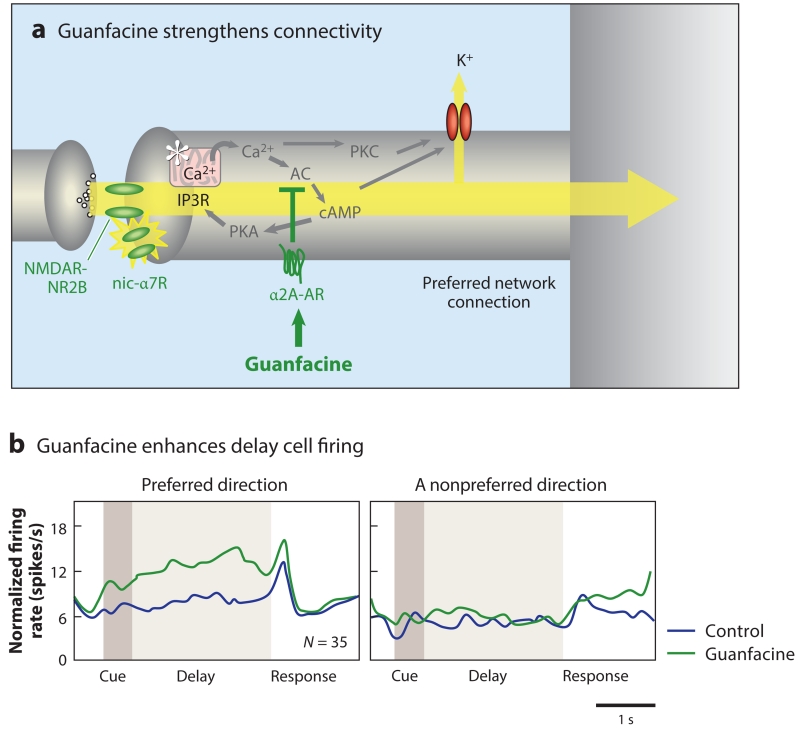
Figure 6.
The α2A-AR agonist guanfacine strengthens dlPFC network connections and enhances dlPFC network firing. (a) A schematic illustration of guanfacine’s actions in the primate dlPFC, engaging postsynaptic α2A-ARs to inhibit feedforward cAMP-calcium-K+ channel signaling and strengthen NMDAR connections. (b) Guanfacine increases the firing of delay cells for their preferred direction. The normalized mean firing rate of 35 delay cells under control conditions (blue) and following iontophoresis of guanfacine (green) are shown, as are the neurons’ preferred direction and their nonpreferred direction opposite to the preferred direction. Guanfacine improves a variety of PFC cognitive functions and is now in widespread clinical use. Abbreviations: AC, adenylyl cyclase; AR, adrenergic receptor; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; dlPFC, dorsolateral PFC; IP3R, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor; nic-α7R, nicotinic α7 receptor; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartate; NMDAR, NMDA receptor; PFC, prefrontal cortex; PKA/PKC, protein kinase A/C.