Table 1.
Effect of ligand and oxidant in gold-catalyzed oxidative C–H arylation of isoxazole 1a.a
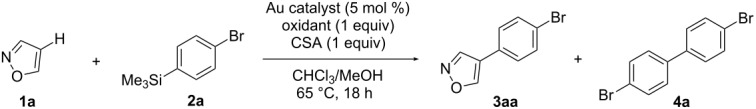 | ||||
| Entry | Au catalyst | Oxidant | Yield [%]b | |
| 3aa | 4a | |||
| 1 | AuCl(PPh3) | IBA | 10 | 7 |
| 2 | AuCl(IPr) | IBA | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | AuCl(PyC) | IBA | 30 | 12 |
| 4 | AuCl(PyC) | PhI(OAc)2 | 4 | 5 |
| 5 | AuCl(PyC) | PhI(OCOCF3)2 | 3 | 4 |
| 6c | AuCl(PyC) | PhI(OH)(OTs) | 9 | 5 |
| 7d | AuCl(PyC) | IBA | 13 | 5 |
| 8c | AuCl(PyC) | IBA | 0 | 9 |
| 9e | AuCl(PyC) | IBA | 3 | 36 |
aReaction conditions: 1a (0.20 mmol), 2a (0.20 mmol), Au catalyst (5 mol %), oxidant (0.20 mmol), (+)-10-camphorsulfonic acid (CSA, 0.20 mmol), CHCl3/MeOH (10:1, 1.1 mL), 65 °C. bDetermined by GC analysis with n-nonane as an internal standard. cWithout CSA. dTsOH·H2O was used instead of CSA. eCHCl3 (1.0 mL) was used as solvent.
