Figure 1.
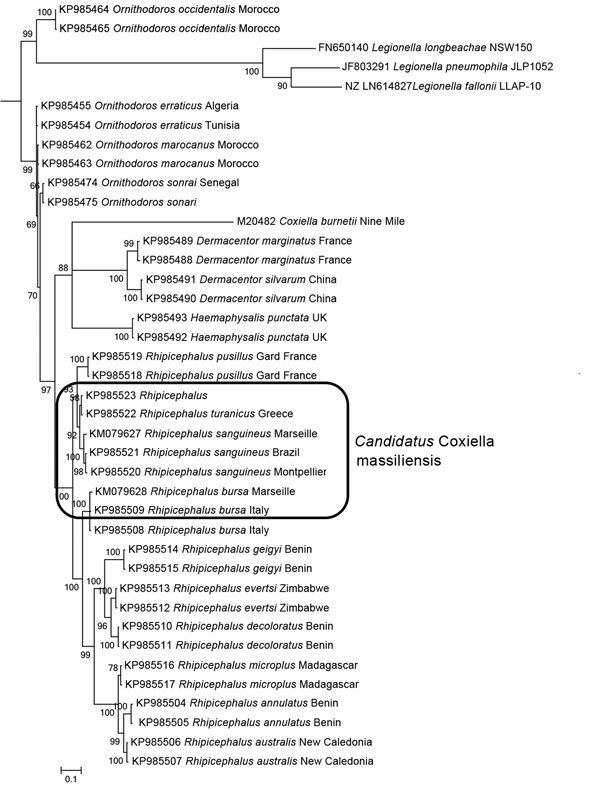
Phylogenetic tree based on GroEL sequences including Coxiella-like strains of bacteria from ticks, Coxiella burnetii reference strains, and bacterial outgroups. GroEL gene sequences (Technical Appendix Table 2) were aligned by using ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/), and phylogenetic inferences were obtained by using Bayesian phylogenetic analysis with TOPALi 2.5 software (http://www.topali.org/) and the integrated MrBayes (http://mrbayes.sourceforge.net/) application with the HKY+Г (Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano plus gamma) substitution model for the first and third codons and the JC model for the second codon. GenBank accession numbers are indicated first, followed by the tick host. Numbers at nodes are bootstrap values obtained by repeating the analysis 100 times to generate a majority consensus tree. The final dataset contained 576 positions. Scale bar indicates 10% nucleotide sequence divergence.
